How Do You Make A Supersaturated Solution
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
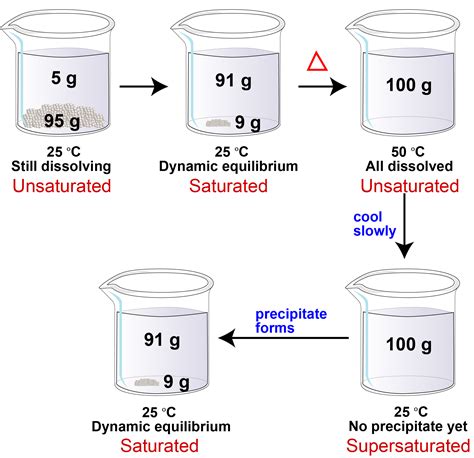
Table of Contents
How to Make a Supersaturated Solution: A Comprehensive Guide
Supersaturated solutions, those holding more solute than theoretically possible under normal conditions, are fascinating examples of physical chemistry in action. Understanding how to create them unlocks a world of possibilities, from stunning crystal growth experiments to practical applications in various industries. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of supersaturation, exploring the process, underlying principles, and safety considerations involved in creating these intriguing solutions.
Understanding Supersaturation: Beyond Saturation
Before diving into the practical aspects, let's establish a firm grasp of the fundamental concepts. A saturated solution contains the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a given solvent at a specific temperature and pressure. Adding more solute to a saturated solution will simply result in undissolved solute precipitating out.
A supersaturated solution, however, defies this equilibrium. It holds more solute than a saturated solution at the same temperature and pressure. This unstable state is a delicate balance, and any slight disturbance can trigger the excess solute to crystallize out, often resulting in a dramatic display of rapid crystal growth.
Factors Affecting Supersaturation
Several key factors influence the creation and stability of supersaturated solutions:
1. Temperature: The Key Player
Temperature plays a pivotal role. Most solids exhibit increased solubility in liquids as temperature rises. This principle forms the bedrock of supersaturation preparation. By dissolving a large amount of solute in a hot solvent, you create a solution that's supersaturated when cooled. As the temperature drops, the solubility decreases, yet the solute remains dissolved, creating the supersaturated state.
2. Solvent Selection: Matching the Solute
The choice of solvent is crucial. The solvent must effectively dissolve the solute at elevated temperatures. Water is a common and versatile solvent, but other solvents, such as ethanol or specialized organic solvents, might be necessary depending on the solute. Careful consideration of the solute-solvent interaction is critical for successful supersaturation.
3. Solute Purity: Avoiding Impurities
High solute purity minimizes nucleation sites. Nucleation sites are microscopic imperfections or impurities that act as starting points for crystal growth. Impurities can prematurely trigger crystallization from a supersaturated solution, hindering the creation of a truly supersaturated state. Using high-purity solutes increases the chances of achieving a stable supersaturated solution.
4. Controlled Cooling: Slow and Steady
Gentle and controlled cooling is essential. Rapid cooling can introduce numerous nucleation sites, leading to immediate precipitation rather than a stable supersaturated solution. Slow, gradual cooling allows the solute molecules to remain in solution even as the solubility decreases. Techniques like placing the solution in an insulated container can help maintain a controlled cooling rate.
5. Avoiding Disturbances: Maintaining Stability
Once a supersaturated solution is prepared, it's crucial to minimize disturbances. Shaking, stirring, or even vibrations can introduce nucleation sites and trigger crystallization. The supersaturated solution should be handled gently and kept in a stable environment.
Methods for Creating Supersaturated Solutions
Several methods can achieve supersaturation. The choice of method often depends on the specific solute and desired outcome.
Method 1: Heating and Cooling
This is the most common method. The steps are as follows:
- Heat the Solvent: Heat the chosen solvent (often water) to near its boiling point.
- Add Solute Gradually: Slowly add the solute, stirring continuously to ensure complete dissolution. Continue adding solute until no more will dissolve, indicating saturation.
- Add Excess Solute: Carefully add a small amount of extra solute, ensuring it also dissolves. This extra solute is what will create the supersaturation.
- Slow Cooling: Allow the solution to cool very slowly, undisturbed, ideally to room temperature or below. Avoid shaking or disturbing the solution during cooling.
Method 2: Evaporation
This method relies on solvent evaporation to increase the solute concentration:
- Prepare a Saturated Solution: Prepare a saturated solution of the solute at room temperature.
- Slow Evaporation: Allow the solvent to evaporate slowly over time. This method requires patience; it can take days or even weeks depending on the solvent and solute. A covered container with a small opening can help control the evaporation rate.
- Monitor Carefully: Regularly monitor the solution. Once the solution becomes supersaturated, it is very susceptible to crystallization.
Method 3: Seeding
This method uses a small "seed" crystal to initiate controlled crystallization from a supersaturated solution:
- Prepare a Supersaturated Solution: Prepare a supersaturated solution using the heating and cooling method.
- Introduce Seed Crystal: Introduce a small, pure crystal of the solute into the supersaturated solution. This seed crystal provides a nucleation site for controlled crystal growth.
- Observe Crystal Growth: Observe the controlled growth of crystals from the seed crystal.
Safety Precautions: Handling with Care
Working with supersaturated solutions requires careful attention to safety:
- Eye Protection: Always wear safety goggles to protect your eyes from potential splashes.
- Appropriate Clothing: Wear appropriate lab attire, including a lab coat.
- Proper Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area, especially when using solvents with strong odors.
- Heat Safety: Exercise caution when heating solvents, avoiding overheating or burns.
- Disposal: Dispose of solutions properly according to local regulations. Supersaturated solutions may not be simply poured down the drain.
Applications of Supersaturated Solutions
Supersaturated solutions find applications in diverse fields:
- Crystal Growth: Producing high-quality single crystals for various applications, including optics and electronics.
- Pharmaceuticals: Formulating stable and readily absorbable drug delivery systems.
- Food Science: Creating confectionery products with desired texture and appearance.
- Chemical Engineering: Developing controlled precipitation and crystallization processes.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Several challenges may arise during supersaturation preparation:
- Premature Crystallization: This can be due to rapid cooling, impurities, or disturbances. Try slower cooling, using purer solutes, and minimizing disturbances.
- Incomplete Dissolution: Ensure the solute fully dissolves at the elevated temperature. Consider using a higher temperature or longer heating time.
- Instability: A highly unstable supersaturated solution may indicate an unsuitable solute-solvent combination. Experiment with different solvents or solutes.
Conclusion: Unveiling the Wonders of Supersaturation
Mastering the art of creating supersaturated solutions unveils a world of scientific wonder and practical applications. By understanding the fundamental principles, carefully controlling the process, and taking necessary safety precautions, you can unlock the potential of these unique and unstable solutions. From breathtaking crystal growth demonstrations to sophisticated industrial applications, supersaturated solutions remain a fascinating subject of study and exploration in chemistry and related fields. The techniques described here provide a solid foundation for embarking on your own experiments with supersaturation, fostering a deeper appreciation for the fascinating world of solution chemistry. Remember to always prioritize safety and responsible laboratory practices. Happy experimenting!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Does The Diagonals Of A Parallelogram Bisect Each Other
May 09, 2025
-
Is 88 A Prime Or Composite Number
May 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Bonds Is The Weakest
May 09, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 36 And 54
May 09, 2025
-
Compare And Contrast Weathering And Erosion
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Make A Supersaturated Solution . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.