How Do You Calculate Mole Fraction
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 6 min read
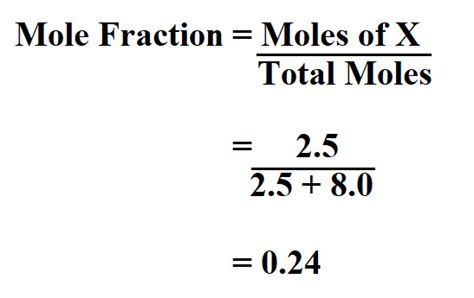
Table of Contents
How to Calculate Mole Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Mole fraction, a fundamental concept in chemistry, represents the ratio of the number of moles of a particular component in a mixture to the total number of moles of all components in that mixture. Understanding how to calculate mole fraction is crucial for various applications, from determining the composition of solutions to analyzing chemical reactions and understanding gas mixtures. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the calculation process, providing examples and addressing common challenges.
Understanding the Basics: Moles and Mole Fraction
Before diving into calculations, let's solidify our understanding of the key terms:
-
Mole (mol): The mole is the International System of Units (SI) unit for the amount of substance. It represents a specific number of particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.), equal to Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10<sup>23</sup>).
-
Mole Fraction (χ): The mole fraction of a component (let's say, component A) in a mixture is defined as the number of moles of that component divided by the total number of moles of all components in the mixture. Mathematically:
χ<sub>A</sub> = n<sub>A</sub> / n<sub>total</sub>
Where:
- χ<sub>A</sub> is the mole fraction of component A.
- n<sub>A</sub> is the number of moles of component A.
- n<sub>total</sub> is the total number of moles of all components in the mixture.
Calculating Mole Fraction: Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating mole fraction involves these key steps:
-
Determine the number of moles of each component: This often requires using the molar mass of each substance. The molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance and is typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). You can find molar mass values on periodic tables or in chemical handbooks. The formula for calculating the number of moles is:
n = m / M
Where:
- n is the number of moles.
- m is the mass of the substance (in grams).
- M is the molar mass of the substance (in g/mol).
-
Calculate the total number of moles: Sum the number of moles of all components in the mixture.
-
Calculate the mole fraction of each component: Divide the number of moles of each individual component by the total number of moles calculated in step 2.
Example Calculation: Binary Mixture
Let's consider a simple binary mixture of ethanol (C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>5</sub>OH) and water (H<sub>2</sub>O). Suppose we have 46 grams of ethanol and 18 grams of water.
-
Calculate moles of ethanol:
- Molar mass of ethanol (C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>5</sub>OH) ≈ 46 g/mol
- n<sub>ethanol</sub> = m<sub>ethanol</sub> / M<sub>ethanol</sub> = 46 g / 46 g/mol = 1 mol
-
Calculate moles of water:
- Molar mass of water (H<sub>2</sub>O) ≈ 18 g/mol
- n<sub>water</sub> = m<sub>water</sub> / M<sub>water</sub> = 18 g / 18 g/mol = 1 mol
-
Calculate total moles:
- n<sub>total</sub> = n<sub>ethanol</sub> + n<sub>water</sub> = 1 mol + 1 mol = 2 mol
-
Calculate mole fractions:
- Mole fraction of ethanol (χ<sub>ethanol</sub>): 1 mol / 2 mol = 0.5
- Mole fraction of water (χ<sub>water</sub>): 1 mol / 2 mol = 0.5
Therefore, in this mixture, both ethanol and water have a mole fraction of 0.5. Notice that the sum of all mole fractions in a mixture always equals 1. This serves as a useful check for your calculations.
Example Calculation: Ternary Mixture (Three Components)
Let's analyze a more complex scenario: a ternary mixture containing 10 grams of methane (CH<sub>4</sub>), 28 grams of nitrogen (N<sub>2</sub>), and 32 grams of oxygen (O<sub>2</sub>).
-
Calculate moles of each component:
-
Molar mass of methane (CH<sub>4</sub>) ≈ 16 g/mol
-
n<sub>methane</sub> = 10 g / 16 g/mol ≈ 0.625 mol
-
Molar mass of nitrogen (N<sub>2</sub>) ≈ 28 g/mol
-
n<sub>nitrogen</sub> = 28 g / 28 g/mol = 1 mol
-
Molar mass of oxygen (O<sub>2</sub>) ≈ 32 g/mol
-
n<sub>oxygen</sub> = 32 g / 32 g/mol = 1 mol
-
-
Calculate total moles:
- n<sub>total</sub> = n<sub>methane</sub> + n<sub>nitrogen</sub> + n<sub>oxygen</sub> ≈ 0.625 mol + 1 mol + 1 mol = 2.625 mol
-
Calculate mole fractions:
- Mole fraction of methane (χ<sub>methane</sub>): 0.625 mol / 2.625 mol ≈ 0.238
- Mole fraction of nitrogen (χ<sub>nitrogen</sub>): 1 mol / 2.625 mol ≈ 0.381
- Mole fraction of oxygen (χ<sub>oxygen</sub>): 1 mol / 2.625 mol ≈ 0.381
The sum of the mole fractions (0.238 + 0.381 + 0.381 ≈ 1) confirms the accuracy of our calculations.
Dealing with More Complex Scenarios
The principles remain the same even when dealing with more complex mixtures involving numerous components or those expressed in different units (e.g., volume percentage, mass percentage). The key is to always convert everything to moles before applying the mole fraction formula.
Converting from Mass Percentage to Mole Fraction:
If you're given the composition of a mixture in mass percentages, you'll need to first convert these percentages to masses (assuming a total mass of 100g for simplification), and then follow the steps outlined above for calculating the number of moles and subsequently the mole fraction.
Converting from Volume Percentage to Mole Fraction:
For gas mixtures, volume percentages can be directly converted to mole fractions under ideal conditions (using the Ideal Gas Law). However, this isn't generally true for liquid solutions. Volume percentages of liquids require conversion to masses using the densities of the components and then following the typical steps for mole fraction calculations.
Applications of Mole Fraction
Mole fraction plays a vital role in numerous chemical and physical applications:
-
Chemical Thermodynamics: Mole fraction is frequently used in expressing equilibrium constants and activity coefficients, both crucial concepts in thermodynamics.
-
Solution Chemistry: Describing the composition of solutions and understanding the properties of mixtures, such as vapor pressure and boiling point elevation, often involves mole fraction.
-
Gas Mixtures: In analyzing the composition of gas mixtures, particularly in atmospheric chemistry or industrial processes, mole fraction simplifies calculations.
-
Reaction Stoichiometry: Calculating the amounts of reactants and products in chemical reactions often involves using mole fraction to represent the composition of reacting mixtures.
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting
Several common errors can arise when calculating mole fraction:
-
Incorrect molar mass: Double-check the molar mass of each component to ensure accuracy. The slightest error here will propagate throughout the calculation.
-
Unit inconsistencies: Ensure all units are consistent (grams for mass, g/mol for molar mass).
-
Arithmetic errors: Carefully review your calculations to avoid simple mistakes.
-
Forgetting to convert: Always ensure you've converted mass percentages or volume percentages to moles before calculating mole fractions.
-
Incorrect summation: Double check your addition of moles to obtain the total number of moles.
By paying close attention to these details, you can significantly reduce the chance of errors and arrive at accurate mole fraction values.
Conclusion
Calculating mole fraction is a fundamental skill in chemistry and related fields. While the underlying principle is straightforward (moles of component/total moles), careful attention to detail and consistent units are crucial for accuracy. Understanding the steps outlined in this guide, along with the example calculations, will equip you to confidently tackle a wide range of mole fraction problems, regardless of the complexity of the mixture. Remember to always check your work – the sum of all mole fractions should always equal one. This provides a final verification step in your calculation process.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches Is 50 Cm
Mar 04, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 48 Inches
Mar 04, 2025
-
How To Find The Perimeter Of A Parallelogram
Mar 04, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does A Rectangle Have
Mar 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Is Correct
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Calculate Mole Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
