How Are Rectangles And Squares Alike
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
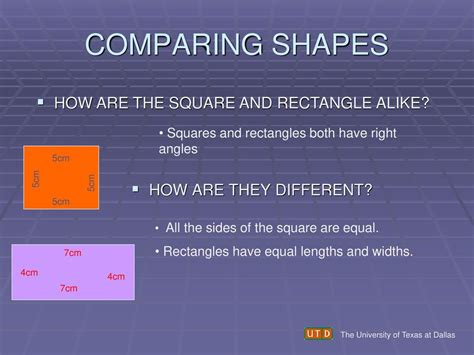
Table of Contents
How Are Rectangles and Squares Alike? Exploring the Similarities Between Two Fundamental Shapes
Squares and rectangles. These two geometric shapes are fundamental building blocks of geometry, appearing everywhere from architecture and design to everyday objects. While they might appear distinct at first glance, a closer examination reveals a surprising number of shared characteristics. Understanding these similarities is key to grasping fundamental geometric principles and solidifying your understanding of shapes. This in-depth exploration will delve into the similarities between rectangles and squares, highlighting their shared attributes and subtly differentiating features.
Shared Properties: The Foundation of Similarity
At their core, rectangles and squares share several defining characteristics. These common properties lay the groundwork for understanding their relationship and highlighting why they are often grouped together in geometric discussions.
1. Four Sides & Four Angles: The Basic Framework
Both rectangles and squares are quadrilaterals, meaning they are polygons with four sides. This fundamental similarity forms the basis for their classification and further comparisons. This shared characteristic provides a starting point for exploring their other common attributes.
2. Opposite Sides are Parallel and Equal: A Defining Parallelism
A critical similarity lies in the parallelism and equality of their opposite sides. In both rectangles and squares, opposite sides are parallel to each other, meaning they never intersect even if extended infinitely. Furthermore, opposite sides are equal in length. This property is crucial in defining their geometric properties and differentiates them from other quadrilaterals like trapezoids or irregular quadrilaterals.
3. Sum of Interior Angles: Always 360 Degrees
Regardless of their size or proportions, both rectangles and squares possess a consistent sum of their interior angles. The sum of the interior angles of any quadrilateral is always 360 degrees. This unwavering characteristic is an important geometric property shared by all quadrilaterals, including both rectangles and squares. It underscores their fundamental connection within the broader family of quadrilaterals.
4. Existence of Diagonals: Connecting Opposite Corners
Both shapes possess diagonals that connect opposite corners. These diagonals exhibit specific properties within each shape, but their existence itself is a shared attribute. The study of these diagonals can further illuminate the relationship between squares and rectangles.
Where They Differ: Subtle Distinctions
While sharing many similarities, subtle distinctions set squares apart from the broader category of rectangles. Understanding these differences clarifies the specific characteristics that define each shape.
1. Angle Measurement: The Defining Difference
The most significant difference lies in their angles. While both possess four angles, rectangles have four right angles (90 degrees), and squares also have four right angles (90 degrees). This might seem redundant, but it highlights the key distinction: all squares are rectangles, but not all rectangles are squares.
2. Side Lengths: The Square's Unique Feature
The crucial differentiating factor is side length. Rectangles have two pairs of equal and parallel sides, but the lengths of these pairs are not necessarily the same. This means that a rectangle can be long and thin or nearly square, but it doesn't have to have all sides equal. In contrast, a square has all four sides equal in length. This equal side length is the defining characteristic that separates squares from the broader group of rectangles.
3. Diagonals: Length and Angle of Intersection
While both shapes possess diagonals, their properties differ subtly. In a rectangle, the diagonals are equal in length, but they do not necessarily bisect each other at a right angle. However, in a square, the diagonals are equal in length and bisect each other at a right angle, forming four congruent right-angled isosceles triangles. This demonstrates the increased symmetry inherent in a square.
4. Symmetry: A Higher Level of Order in the Square
Squares exhibit a higher degree of symmetry compared to rectangles. Squares possess both rotational symmetry (they can be rotated by 90, 180, and 270 degrees and still look the same) and reflectional symmetry (they can be reflected across several axes and remain unchanged). Rectangles possess reflectional symmetry across two axes, but their rotational symmetry is limited to 180 degrees. This enhanced symmetry in squares reflects their more regular and balanced structure.
Practical Applications: Seeing the Shapes in Action
Understanding the similarities and differences between squares and rectangles has far-reaching implications across various disciplines. These shapes are fundamental to numerous practical applications, from architecture and engineering to everyday design.
1. Architecture and Construction: Building with Squares and Rectangles
Squares and rectangles are ubiquitous in architecture and construction. Buildings often incorporate rectangular rooms, windows, and doors for efficiency and structural integrity. Squares, due to their inherent stability, are often used in foundations and supporting structures. The ability to easily calculate areas and perimeters of these shapes makes them ideal for planning and construction.
2. Graphic Design and Visual Arts: Creating Visual Balance
In graphic design, the use of squares and rectangles creates visual balance and order. They provide a stable framework for arranging elements and establishing clear visual hierarchies. Squares, with their inherent symmetry, often serve as focal points, while rectangles are used to create flow and organization.
3. Everyday Objects: From Boxes to Screens
From the rectangular screen of your computer to the square tiles on your floor, these shapes surround us in everyday objects. Their prevalence highlights their practical applications in mass production and design. The simple geometry allows for efficient manufacturing and ease of use.
Advanced Considerations: Exploring Further Connections
The relationship between squares and rectangles extends beyond basic geometric principles. Exploring more advanced mathematical concepts reveals further connections and underscores the significance of these seemingly simple shapes.
1. Area Calculation: A Simple Formula
Calculating the area of both rectangles and squares is straightforward. The formula for the area of a rectangle is length × width, while for a square, it simplifies to side × side (or side²). This simple formula highlights the inherent relationship between the two shapes – a square being a special case of a rectangle where length and width are equal.
2. Perimeter Calculation: Another Shared Simplicity
Calculating the perimeter (the distance around the shape) is also similarly straightforward. The perimeter of a rectangle is 2(length + width), while for a square it is 4 × side. This again demonstrates the square's status as a specialized rectangle.
3. Transformations in Geometry: Exploring the Relationship Through Movement
Transformations like rotations, reflections, and translations can be applied to both squares and rectangles. Understanding how these transformations affect the shape and its properties provides deeper insights into their geometric relationships.
4. Tessellations: Covering Surfaces with Squares and Rectangles
Both squares and rectangles can be used to create tessellations – patterns of shapes that cover a surface without overlapping or leaving gaps. The ability to tessellate is another shared property that underlines their suitability for various design applications.
Conclusion: Understanding the Shared Heritage
In conclusion, the similarities between rectangles and squares are significant and far-reaching. They share fundamental properties like four sides, parallel and equal opposite sides, and a sum of interior angles of 360 degrees. However, the critical distinction lies in the equal length of all four sides in a square, a defining characteristic absent in the broader category of rectangles. Understanding both the shared features and the subtle differences is crucial for a comprehensive grasp of geometric principles and their applications across various fields. The exploration of squares and rectangles offers a foundational understanding of geometric relationships and their practical implications in the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
7 Continents And 5 Oceans List
Mar 25, 2025
-
Dissolving Of Salt In Water Physical Or Chemical
Mar 25, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 5
Mar 25, 2025
-
Gravitational Force Between The Earth And The Sun
Mar 25, 2025
-
5 Letter Words Starting With Ad
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Are Rectangles And Squares Alike . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
