Heat Of Combustion Of Benzoic Acid
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
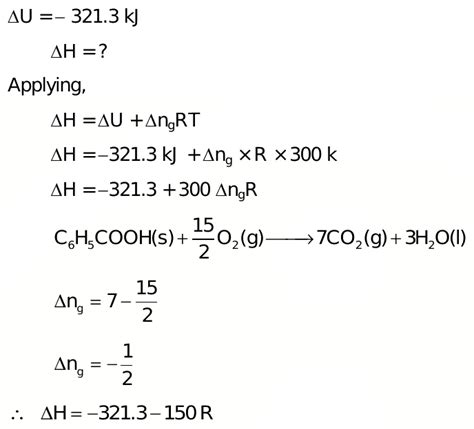
Table of Contents
- Heat Of Combustion Of Benzoic Acid
- Table of Contents
- The Heat of Combustion of Benzoic Acid: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Heat of Combustion
- Determining the Heat of Combustion of Benzoic Acid
- Bomb Calorimetry: The Gold Standard
- The Accepted Value of the Heat of Combustion of Benzoic Acid
- Significance and Applications
- Factors Affecting the Heat of Combustion
- Beyond Benzoic Acid: Other Calorimetric Standards
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Heat of Combustion of Benzoic Acid: A Comprehensive Guide
Benzoic acid, a simple aromatic carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C₇H₆O₂, holds a significant place in the world of thermochemistry. Its precisely known heat of combustion makes it an invaluable standard for calibrating calorimeters – instruments used to measure heat changes in chemical reactions. This article delves deep into the heat of combustion of benzoic acid, exploring its determination, significance, applications, and associated factors.
Understanding Heat of Combustion
The heat of combustion, also known as the enthalpy of combustion, represents the amount of heat released when one mole of a substance undergoes complete combustion in excess oxygen. This process typically involves the complete oxidation of the substance to form carbon dioxide (CO₂), water (H₂O), and other relevant products. The heat released is a crucial measure of a substance's energy content. It's expressed in units of kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol).
For benzoic acid, the combustion reaction can be represented as:
C₇H₆O₂(s) + 15/2 O₂(g) → 7CO₂(g) + 3H₂O(l)
This equation shows that one mole of solid benzoic acid reacts with 15/2 moles of gaseous oxygen to produce 7 moles of gaseous carbon dioxide and 3 moles of liquid water. The heat released during this reaction is the heat of combustion of benzoic acid.
Determining the Heat of Combustion of Benzoic Acid
The accurate determination of the heat of combustion of benzoic acid is crucial for its use as a calorimetric standard. Several methods are employed, with bomb calorimetry being the most prevalent.
Bomb Calorimetry: The Gold Standard
Bomb calorimetry involves burning a precisely weighed sample of benzoic acid in a sealed, oxygen-filled bomb within a water bath. The heat released by the combustion raises the temperature of the water bath, and this temperature change is carefully measured using a highly sensitive thermometer. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (the bomb, water, and its surroundings) must be accurately known beforehand.
Steps involved in Bomb Calorimetry:
-
Sample Preparation: A precisely weighed amount of benzoic acid (typically around 1 gram) is compressed into a pellet and placed inside the bomb. A small fuse wire, usually made of nickel or iron, is also included to ignite the sample.
-
Bomb Assembly: The bomb is sealed and filled with pure oxygen under high pressure. This ensures complete combustion of the benzoic acid.
-
Calorimeter Calibration: The calorimeter's heat capacity (C<sub>cal</sub>) is determined using a known standard, such as benzoic acid itself, or another substance with a well-established heat of combustion.
-
Ignition and Temperature Measurement: The sample is ignited electrically, and the resulting temperature rise (ΔT) of the water bath is precisely measured.
-
Calculations: The heat of combustion (ΔH<sub>c</sub>) is calculated using the following equation:
ΔH<sub>c</sub> = - (C<sub>cal</sub> × ΔT) / moles of benzoic acid
The negative sign indicates that heat is released (exothermic reaction).
Key Considerations in Bomb Calorimetry:
- Purity of Benzoic acid: Impurities can significantly affect the measured heat of combustion. High-purity benzoic acid is essential for accurate results.
- Complete Combustion: Ensuring complete combustion of the sample is critical. Insufficient oxygen can lead to incomplete combustion and inaccurate results.
- Heat Loss: Minimizing heat loss to the surroundings is crucial for accurate temperature measurements. Proper insulation and efficient stirring of the water bath help reduce heat loss.
- Calibration Accuracy: The accuracy of the calorimeter's heat capacity determination directly impacts the accuracy of the final result.
The Accepted Value of the Heat of Combustion of Benzoic Acid
The accepted value for the heat of combustion of benzoic acid at standard conditions (298.15 K and 1 atm) is -26.43 kJ/g or -3227 kJ/mol. This value is based on extensive experimentation and serves as a universally accepted standard for calorimeter calibration. Slight variations might be reported due to different experimental conditions and methodologies, but they generally remain within a narrow range.
Significance and Applications
The accurately known heat of combustion of benzoic acid is crucial for several reasons:
-
Calorimeter Calibration: As mentioned earlier, it's the primary standard for calibrating bomb calorimeters, ensuring the accuracy of measurements for other substances.
-
Thermochemical Studies: It serves as a reference point for thermodynamic calculations and comparisons in various thermochemical studies.
-
Energy Content Determination: The heat of combustion provides a direct measure of the energy content of benzoic acid and other substances, which is relevant in fields like fuel science and energy production.
-
Industrial Applications: Benzoic acid is used as a preservative in food and pharmaceuticals. Understanding its heat of combustion contributes to process optimization and safety in industrial applications.
-
Research and Development: The heat of combustion data helps researchers in developing new materials with specific energy characteristics.
Factors Affecting the Heat of Combustion
Several factors can influence the measured heat of combustion of benzoic acid:
-
Purity of the sample: As mentioned before, impurities will alter the measured value. High-purity benzoic acid is crucial.
-
Oxygen pressure: Insufficient oxygen can lead to incomplete combustion, resulting in a lower measured heat of combustion.
-
Temperature and pressure: Deviations from standard temperature and pressure (STP) can slightly affect the results. Corrections are often applied to account for these variations.
-
Water content: The presence of water in the sample or in the bomb can also affect the measurement, leading to discrepancies.
-
Heat capacity of the calorimeter: An inaccurate determination of the calorimeter's heat capacity will directly impact the final result.
Beyond Benzoic Acid: Other Calorimetric Standards
While benzoic acid is the most common standard, other substances are also used for calorimeter calibration, particularly for specialized applications. These include naphthalene, succinic acid, and certain hydrocarbons. The choice of standard depends on the specific needs and limitations of the experiment.
Conclusion
The heat of combustion of benzoic acid is a fundamental quantity in thermochemistry. Its precisely known value makes it the gold standard for calibrating calorimeters, ensuring the accuracy of heat measurements for a wide range of substances. Understanding its determination, significance, and the factors that influence its measurement is crucial for anyone working in fields involving thermochemistry, calorimetry, and energy studies. The ongoing refinement of experimental techniques and the development of advanced calorimetric instrumentation continue to improve the accuracy and precision of these crucial measurements. The information provided in this comprehensive guide should equip readers with a detailed understanding of this important chemical property.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percent Of 50 Is 20
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Long Is 72 Inches In Feet
Mar 15, 2025
-
5 Letter Words That Start With Par
Mar 15, 2025
-
120 Square Meters To Square Feet
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is 29 Degrees Celsius In Fahrenheit
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Heat Of Combustion Of Benzoic Acid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
