Heart Chamber With The Thickest Wall
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 6 min read
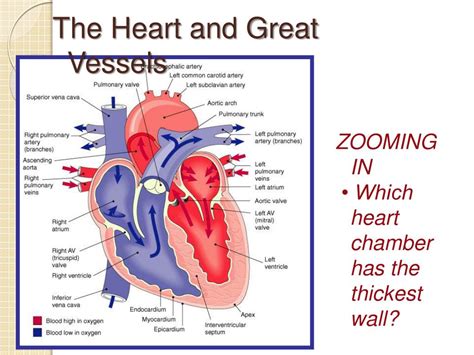
Table of Contents
The Heart Chamber with the Thickest Wall: Understanding the Left Ventricle
The human heart, a tireless engine driving our circulatory system, is a marvel of biological engineering. Composed of four chambers – two atria and two ventricles – each plays a crucial role in pumping blood throughout the body. While all chambers contribute to the seamless functioning of the cardiovascular system, one stands out for its robust structure: the left ventricle. This chamber boasts the thickest wall of all, a testament to its demanding role in propelling oxygenated blood to the entire body.
The Anatomy of a Powerful Pump: Why the Left Ventricle Needs Thick Walls
Understanding why the left ventricle possesses the thickest wall requires examining its function. Unlike the right ventricle, which pumps blood only to the lungs (a relatively short distance), the left ventricle faces a far more strenuous task. It's responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs, through the aorta, and to every organ and tissue in the body. This requires significantly higher pressure and force.
The Pressure Differential: A Key Factor
The pressure differential between the left ventricle and the systemic circulation is dramatically higher than that between the right ventricle and the pulmonary circulation. The systemic circulation encompasses the entire body, requiring considerably more pressure to overcome the resistance of the extensive network of blood vessels. This higher pressure necessitates a stronger, thicker muscular wall to withstand the force generated during each contraction.
Myocardial Structure and Function: A Closer Look
The left ventricular wall is predominantly composed of myocardium, a specialized cardiac muscle tissue. The myocardium's structure is highly organized, with cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells) arranged in a complex network that allows for efficient force generation and coordinated contraction. The increased thickness of the left ventricular myocardium translates directly to a greater number of muscle cells, leading to a more powerful contraction.
The Role of the Left Ventricular Wall Thickness in Maintaining Blood Pressure
The left ventricle's thick wall isn't just about force; it's crucial for maintaining systemic blood pressure. A sufficiently thick wall ensures that blood is ejected forcefully and efficiently into the aorta, establishing the necessary pressure gradient for blood to circulate throughout the body. Compromised left ventricular wall thickness can lead to decreased ejection fraction (the percentage of blood ejected from the ventricle with each contraction) and potentially lead to hypotension (low blood pressure).
Clinical Implications of Left Ventricular Wall Thickness: Hypertrophy and Disease
The thickness of the left ventricular wall isn't static; it can change in response to various physiological and pathological conditions. While a certain degree of increase in wall thickness (physiological hypertrophy) can be an adaptive response to increased workload, excessive thickening (pathological hypertrophy) can be a sign of underlying heart disease.
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH): A Sign of Cardiac Stress
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the mass of the left ventricular myocardium. This can be caused by various factors, including:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure): Chronic high blood pressure forces the left ventricle to work harder to pump blood against increased resistance, leading to thickening of the wall. This is one of the most common causes of LVH.
- Aortic stenosis: Narrowing of the aortic valve restricts blood flow out of the left ventricle, causing the ventricle to work harder to overcome the obstruction, resulting in hypertrophy.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM): This is a genetic condition characterized by thickening of the left ventricular wall, often leading to diastolic dysfunction (impaired ability to relax and fill with blood).
- Chronic kidney disease: Fluid retention and increased blood volume can place extra strain on the heart, contributing to LVH.
- Obstructive sleep apnea: Repeated episodes of low oxygen levels during sleep can stress the cardiovascular system and lead to hypertrophy.
The Dangers of LVH: Heart Failure and Arrhythmias
Excessive left ventricular hypertrophy can lead to several serious complications:
- Heart failure: The thickened heart muscle may become less efficient at pumping blood, leading to heart failure. This can manifest as shortness of breath, fatigue, and edema (swelling).
- Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms can occur due to changes in the electrical conduction system of the hypertrophied heart muscle. These arrhythmias can range from mild palpitations to life-threatening ventricular fibrillation.
- Sudden cardiac death: In severe cases, LVH can increase the risk of sudden cardiac death.
Diagnosing and Managing Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Diagnosing LVH typically involves several tests:
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test provides detailed images of the heart, allowing for measurement of left ventricular wall thickness and assessment of its function.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test measures the heart's electrical activity, which can reveal abnormalities associated with LVH.
- Cardiac MRI: A more detailed imaging technique that provides even more precise measurements of left ventricular mass and function.
Management of LVH focuses on addressing the underlying cause and minimizing the risk of complications. This often involves:
- Lifestyle modifications: These include dietary changes (reducing sodium intake), regular exercise, and weight management.
- Medication: Medications may be prescribed to control blood pressure, reduce heart rate, or improve heart function. These could include ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, or diuretics.
- Cardiac rehabilitation: This program involves supervised exercise and education to help patients improve their cardiovascular health.
- Surgical intervention: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct valve problems or other structural abnormalities contributing to LVH.
The Left Ventricle: A Powerful and Delicate Structure
The left ventricle, with its remarkably thick wall, is a critical component of our cardiovascular system. Its strength and efficiency are essential for maintaining adequate blood flow to all parts of the body. However, the very factors that make it so powerful – its robust muscle and ability to generate high pressure – also make it vulnerable to hypertrophy and associated complications. Understanding the structure and function of the left ventricle, as well as the conditions that can affect its health, is crucial for preventing and managing cardiovascular disease.
Further Exploration: Research and Ongoing Studies
Research into the left ventricle continues to advance our understanding of its complex physiology and pathology. Scientists are actively investigating:
- Novel biomarkers: Identifying new markers that can predict the development and progression of LVH.
- Targeted therapies: Developing more effective treatments to prevent and reverse LVH, focusing on the underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms.
- Advanced imaging techniques: Improving the accuracy and resolution of imaging technologies to better assess left ventricular structure and function.
The ongoing research efforts promise to further refine our understanding and management of left ventricular hypertrophy, improving the lives of millions affected by this prevalent condition. The thicker walls of the left ventricle, while essential for life, underscore the importance of maintaining cardiovascular health through lifestyle choices, regular medical checkups, and timely intervention when necessary. It's a reminder of the remarkable complexity and vulnerability of this vital organ at the heart of our being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Times Does Dna Replicate In Mitosis
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Square Feet Is 400 Square Meters
May 09, 2025
-
First 30 Elements Of Periodic Table
May 09, 2025
-
Breakdown Of Glucose To Pyruvic Acid
May 09, 2025
-
Is Crushing A Can A Physical Change
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Heart Chamber With The Thickest Wall . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.