Give An Example Of An Unbalanced Force
Juapaving
Apr 05, 2025 · 7 min read
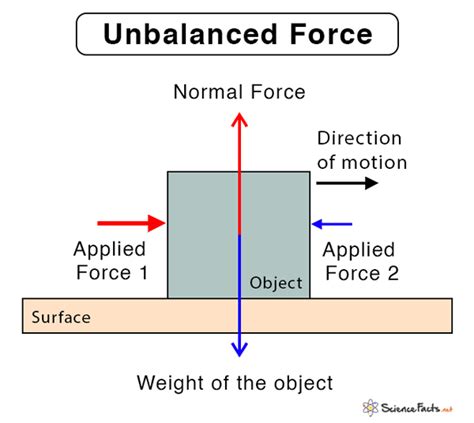
Table of Contents
Unbalanced Forces: A Deep Dive with Real-World Examples
Understanding forces is fundamental to grasping how the physical world works. From the smallest atom to the largest galaxy, forces govern motion, interaction, and change. While balanced forces result in no net change in motion (an object at rest stays at rest, an object in motion stays in motion at the same speed and direction), unbalanced forces are the drivers of acceleration, deceleration, and changes in direction. This article will delve into the concept of unbalanced forces, providing numerous real-world examples and explaining their significance.
What are Unbalanced Forces?
Simply put, unbalanced forces occur when the net force acting on an object is not zero. This means that the sum of all forces acting on the object is not equal to zero, resulting in a change in the object's motion. This change can be a change in speed, direction, or both. Think of it like a tug-of-war: if one team pulls harder than the other, the rope moves—representing a net force and thus, an unbalanced force system.
Key characteristics of unbalanced forces:
- Net force is not zero: The total force acting on an object is not balanced.
- Causes acceleration: Unbalanced forces always result in acceleration, either positive (speeding up), negative (slowing down), or changing direction.
- Changes in motion: The object's state of motion changes – it either speeds up, slows down, or changes direction.
Examples of Unbalanced Forces in Everyday Life
Let's explore various everyday situations where unbalanced forces are at play:
1. Pushing a Shopping Cart
Imagine pushing a shopping cart in a supermarket. You apply a force to the cart, overcoming friction and inertia. This force is greater than the opposing forces of friction and air resistance; thus, it's an unbalanced force, causing the cart to accelerate. If you stop pushing, friction becomes the dominant force, causing the cart to decelerate and eventually stop. This highlights how the dominance of forces shifts, creating a dynamic situation of balanced and unbalanced states.
2. Kicking a Soccer Ball
When you kick a soccer ball, your foot exerts a significant force on the ball. This force significantly outweighs the friction between the ball and the ground, as well as air resistance. The resulting unbalanced force propels the ball forward, accelerating it until other forces, like air resistance and gravity, eventually slow it down. The angle of your kick also influences the direction, further illustrating how unbalanced forces control both speed and direction.
3. Driving a Car
Driving a car is a continuous interplay of balanced and unbalanced forces. When you accelerate, the force from the engine overcomes friction and air resistance, creating an unbalanced force that increases the car's speed. Braking involves applying an unbalanced force in the opposite direction of motion, decelerating the car until it stops. Steering involves applying unbalanced forces to change the direction of the car's motion. Even at a constant speed, subtle adjustments are made to counteract external forces and maintain balance.
4. A Falling Apple
Newton's famous apple falling from a tree perfectly demonstrates unbalanced forces. The primary force acting on the apple is gravity, pulling it downwards towards the Earth. Air resistance opposes this motion but is significantly smaller, resulting in a net downward force. This unbalanced force causes the apple to accelerate towards the ground until it impacts.
5. Riding a Bicycle
Riding a bicycle involves a complex interplay of unbalanced forces. You pedal, generating a forward force that overcomes friction and air resistance. Leaning allows you to apply a sideways force that counteracts the tendency to topple over, keeping you balanced and in control of your direction. Braking involves applying an unbalanced force to slow down the bicycle, creating a deceleration.
6. A Rocket Launching
Rocket launches are dramatic examples of incredibly powerful unbalanced forces. The immense thrust generated by the rocket engines far surpasses the forces of gravity and air resistance. This massive unbalanced force propels the rocket upwards, accelerating it to incredible speeds, overcoming Earth's gravitational pull and eventually escaping Earth's atmosphere.
7. Pulling a Wagon
Imagine pulling a wagon filled with toys. If you pull with enough force to overcome the friction of the wheels on the ground and the resistance of the toys inside, you create an unbalanced force causing the wagon to move. If you stop pulling, friction becomes dominant and the wagon gradually stops.
8. Sliding Down a Slide
The force of gravity pulls you down a slide, overcoming the friction between your body and the slide's surface. This unbalanced force accelerates you downwards until you reach the bottom.
9. Pushing a Swing
Pushing a swing involves applying an unbalanced force to increase its speed. As you push, the force of your push overcomes the forces of friction and gravity, resulting in an acceleration. Once you stop pushing, the swing slows down under the influence of balanced forces until it comes to rest.
Unbalanced Forces and Newton's Laws of Motion
The concept of unbalanced forces is intrinsically linked to Newton's three laws of motion:
-
Newton's First Law (Inertia): An object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This law establishes the baseline—an object's state of motion only changes when an unbalanced force acts on it.
-
Newton's Second Law (F=ma): The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass (F = ma). This law quantifies the relationship between unbalanced force, mass, and acceleration. A larger net force produces a greater acceleration, while a larger mass results in a smaller acceleration for the same net force.
-
Newton's Third Law (Action-Reaction): For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. While this law deals with paired forces, it highlights that an unbalanced force on one object is only possible because of the interaction with another object. For example, when you push a wall (action), the wall pushes back on you (reaction) with an equal and opposite force. However, the wall doesn’t move because it's fixed. Thus the net force on you is unbalanced, but the net force on the wall-Earth system remains balanced.
Understanding the Significance of Unbalanced Forces
Unbalanced forces are crucial in understanding a vast range of phenomena, from the seemingly simple act of walking to the complexities of aerospace engineering. Understanding how unbalanced forces affect motion is essential in:
-
Designing machines and structures: Engineers utilize principles of unbalanced forces to design machines that move, accelerate, decelerate, and change direction. Understanding the interplay of forces ensures the efficiency and safety of these systems.
-
Predicting the trajectory of projectiles: Analyzing the unbalanced forces acting on a projectile—gravity, air resistance, and initial launch force—allows us to predict its path.
-
Explaining celestial motion: The gravitational forces between celestial bodies are examples of unbalanced forces that govern their orbits and interactions.
-
Developing new technologies: Innovations in various fields, from transportation to sports equipment, rely heavily on our understanding and manipulation of unbalanced forces.
Conclusion
Unbalanced forces are the fundamental drivers of change in motion. They are ubiquitous in our everyday lives and play a critical role in numerous scientific and engineering applications. By understanding the characteristics and effects of unbalanced forces, we gain a deeper appreciation for the underlying principles that govern the physical world around us. From the simplest act of pushing a door to the complexities of space travel, the concept of unbalanced force remains central to explaining how things move and interact. This comprehensive exploration of unbalanced forces has illustrated their significance and relevance across diverse contexts, highlighting their pervasive influence on the dynamics of our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Long Is 18cm In Inches
Apr 05, 2025
-
An Amoeba Is A Unicellular Organism
Apr 05, 2025
-
Are The Structural And Functional Units Of The Kidneys
Apr 05, 2025
-
2 5 Km Is How Many Miles
Apr 05, 2025
-
10 Letter Words Ending In Tion
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Give An Example Of An Unbalanced Force . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
