Equidistant From The Vertices Of A Triangle
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
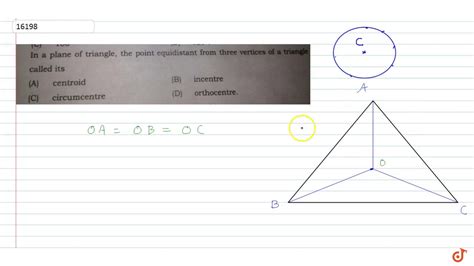
Table of Contents
Equidistant from the Vertices of a Triangle: Exploring the Circumcenter and Its Properties
The concept of a point equidistant from the vertices of a triangle is a fundamental idea in geometry with significant implications in various fields, including surveying, architecture, and computer graphics. This point, known as the circumcenter, holds a unique position within the triangle and possesses fascinating properties. This article delves deep into the circumcenter, exploring its definition, construction, properties, and applications. We'll also explore the relationship between the circumcenter and other notable points within the triangle, such as the centroid, incenter, and orthocenter.
Defining the Circumcenter
The circumcenter of a triangle is the point where the perpendicular bisectors of the sides of the triangle intersect. This intersection point is equidistant from each of the three vertices of the triangle. The distance from the circumcenter to each vertex is known as the circumradius, and the circle with this radius centered at the circumcenter is called the circumcircle. Every triangle has a unique circumcenter, although its location can vary depending on the shape of the triangle.
Acute, Obtuse, and Right-Angled Triangles: Circumcenter Locations
The location of the circumcenter relative to the triangle depends on the type of triangle:
-
Acute Triangle: In an acute triangle (where all angles are less than 90 degrees), the circumcenter lies inside the triangle.
-
Obtuse Triangle: In an obtuse triangle (where one angle is greater than 90 degrees), the circumcenter lies outside the triangle.
-
Right-Angled Triangle: In a right-angled triangle, the circumcenter lies on the hypotenuse, precisely at its midpoint. This is because the hypotenuse is the diameter of the circumcircle.
Constructing the Circumcenter
Constructing the circumcenter is a straightforward geometrical exercise:
-
Draw the Perpendicular Bisectors: Using a compass, draw the perpendicular bisector of each side of the triangle. Remember that the perpendicular bisector of a line segment is the line that is perpendicular to the segment and passes through its midpoint.
-
Find the Intersection Point: The point where these three perpendicular bisectors intersect is the circumcenter. This point will be equidistant from all three vertices of the triangle.
-
Draw the Circumcircle: Using a compass, set the radius to the distance between the circumcenter and any vertex. Draw a circle with this radius centered at the circumcenter. This circle will pass through all three vertices of the triangle.
This construction demonstrates the fundamental property of the circumcenter: its equidistance from the vertices. This construction can be easily performed using simple geometrical tools, making it accessible for various levels of mathematical understanding.
Properties of the Circumcenter
The circumcenter possesses several important properties, making it a crucial point of reference in various geometrical problems:
-
Equidistance from Vertices: As already stated, this is the defining property – the circumcenter is equidistant from all three vertices of the triangle.
-
Circumradius: The distance from the circumcenter to each vertex is the circumradius (often denoted as R). This radius is a key parameter in many triangle calculations.
-
Circumcircle: The circumcenter is the center of the circumcircle, a circle that passes through all three vertices of the triangle.
-
Relationship to Other Triangle Centers: The circumcenter is related to other notable points within the triangle, forming interesting geometrical relationships and forming the basis for various theorems.
Relationship with Other Notable Triangle Centers
The circumcenter interacts with other important triangle centers in several significant ways:
-
Euler Line: In any triangle that is not equilateral, the circumcenter, centroid (the intersection of medians), and orthocenter (the intersection of altitudes) are collinear. This line is known as the Euler line. The circumcenter is located farthest from the triangle itself on the Euler line.
-
Nine-Point Circle: The nine-point circle is a circle that passes through nine significant points related to the triangle: the midpoints of the sides, the feet of the altitudes, and the midpoints of the segments joining the vertices to the orthocenter. The center of the nine-point circle is the midpoint of the segment connecting the circumcenter and orthocenter.
-
Incenter: The incenter, the center of the inscribed circle, is generally not collinear with the circumcenter, centroid, and orthocenter. However, the distances between these points hold specific relationships defined by various geometrical theorems.
Calculating the Circumradius
The circumradius, R, can be calculated using several formulas, depending on the information available about the triangle:
-
Using the sides and area: R = (abc) / (4K), where a, b, c are the lengths of the sides and K is the area of the triangle. This formula highlights the interplay between the side lengths and area in determining the circumradius.
-
Using the sides and angles: Various trigonometric relationships can be used to calculate the circumradius based on side lengths and angles.
-
Using coordinates: If the coordinates of the vertices are known, the circumcenter's coordinates can be calculated using formulas involving the coordinates of the vertices. This is particularly useful in computational geometry.
Applications of the Circumcenter
The circumcenter and circumcircle find application in various areas:
-
Surveying and Mapping: Determining the circumcenter is crucial in surveying to locate a point equidistant from three known points, aiding in accurate land measurement and mapping.
-
Architecture and Engineering: The concept of equidistance from vertices is utilized in architectural design and structural engineering for creating symmetrical and stable structures.
-
Computer Graphics: In computer graphics and game development, the circumcenter is used to calculate the circle that circumscribes a triangle, helpful in various rendering and collision detection algorithms.
-
Astronomy: While less directly applied, the underlying principles of equidistance are related to calculations involving celestial bodies and their relative positions.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
The circumcenter's properties extend beyond the basic concepts explored above. Further exploration could involve:
-
Trilinear Coordinates: Expressing the circumcenter's position using trilinear coordinates provides a more nuanced understanding of its location within the triangle's coordinate system.
-
Complex Numbers in Geometry: Utilizing complex numbers for representing points and lines allows for elegant solutions and proofs related to the circumcenter and other triangle centers.
-
Non-Euclidean Geometry: The concept of equidistance and circumcenters can be extended to non-Euclidean geometries, leading to fascinating results and challenging problems.
-
Generalizations to Higher Dimensions: The concept can be generalized to higher dimensional analogues of triangles (tetrahedrons, etc.), leading to more complex, yet similar, geometric constructions.
Conclusion
The circumcenter of a triangle, a point equidistant from its vertices, holds a significant place in geometry. Its properties, construction, and relationships with other triangle centers provide a rich tapestry of geometrical concepts and applications. Understanding the circumcenter is essential for anyone interested in geometry, its applications, and its extensions into more advanced mathematical fields. From its straightforward geometrical construction to its sophisticated role in various computational and theoretical applications, the circumcenter continues to be a vital and fascinating topic of study. This detailed exploration provides a strong foundation for further investigation and understanding of this critical point in a triangle's geometry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of 9 12 And 15
Mar 18, 2025
-
Where Does Dna Synthesis Happen In Eukaryotic Cells
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Gcf Using Prime Factorization
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Power And Energy
Mar 18, 2025
-
Where Do Sound Waves Travel Fastest
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Equidistant From The Vertices Of A Triangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
