Difference In Ac And Dc Motor
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
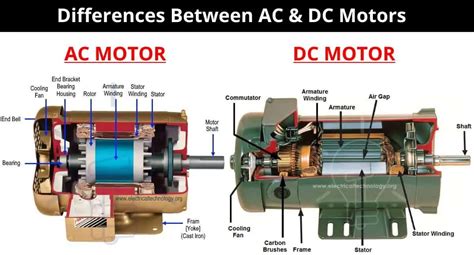
Table of Contents
AC vs. DC Motors: A Deep Dive into the Differences
Choosing the right motor for your application can be crucial. The world of motors is vast, but two primary types dominate the landscape: Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) motors. While both achieve the same fundamental goal – converting electrical energy into mechanical energy – their inner workings, characteristics, and applications differ significantly. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the distinctions between AC and DC motors, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses to help you make informed decisions.
Fundamental Differences: AC vs. DC Power Supply
The most basic difference lies in the type of power they utilize. AC motors operate on alternating current, where the direction of current flow reverses periodically. This reversal is typically at a frequency of 50 or 60 Hertz (Hz), depending on the region. In contrast, DC motors run on direct current, where the current flows in a single direction.
This seemingly simple difference has profound implications for the motor's design, performance, and controllability.
Internal Mechanisms: A Closer Look
The internal construction of AC and DC motors differs considerably due to the contrasting nature of their power sources.
AC Motor Mechanisms:
AC motors primarily rely on the principles of electromagnetism. They typically utilize a rotating magnetic field to induce current in the rotor (the rotating part of the motor), causing it to spin. Several types of AC motors exist, each with its unique characteristics:
-
Induction Motors: These are the most common type of AC motor, known for their simplicity, robustness, and low maintenance. They work on the principle of electromagnetic induction; the stator (stationary part) creates a rotating magnetic field that induces current in the rotor, causing it to rotate. Induction motors are further categorized into squirrel-cage and wound-rotor types.
-
Synchronous Motors: Unlike induction motors, synchronous motors rotate at a speed directly proportional to the frequency of the AC power supply. They require a separate excitation source, often DC, to create their magnetic field. Synchronous motors are known for their precise speed control and high efficiency at constant loads.
-
Servomotors: These are specialized AC motors designed for precise control and high accuracy. Often used in robotics, CNC machines, and other applications requiring fine motor control. Servomotors incorporate feedback mechanisms to maintain precise positioning and speed.
DC Motor Mechanisms:
DC motors utilize a commutator and brushes to convert DC power into rotational motion. The commutator is a segmented cylindrical structure that reverses the current direction in the rotor windings as the rotor spins, ensuring continuous torque production. Brushes make electrical contact with the commutator, delivering current to the rotor windings.
Different types of DC motors exist, each offering unique performance characteristics:
-
Brushed DC Motors: These are the simplest type of DC motor, employing brushes and a commutator for current commutation. They are relatively inexpensive and offer good starting torque, but suffer from brush wear and limited speed control accuracy.
-
Brushless DC Motors (BLDC): These motors eliminate the need for brushes and commutators, achieving higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and better speed control. The commutation process is handled electronically, often using Hall effect sensors. BLDC motors are prevalent in applications demanding high performance and reliability.
Performance Characteristics: A Comparative Analysis
Several key performance characteristics distinguish AC and DC motors:
Speed Control:
-
AC Motors: Speed control in AC motors is generally more complex and less precise than in DC motors, particularly in induction motors. Methods include varying the frequency of the AC power supply (using variable frequency drives or VFDs) or adjusting the voltage.
-
DC Motors: Speed control in DC motors is relatively straightforward, often achieved by adjusting the voltage applied to the motor. This allows for precise speed regulation, making them suitable for applications requiring variable speed control.
Starting Torque:
-
AC Motors: The starting torque of AC motors, particularly induction motors, is typically lower than that of DC motors. However, this can be improved using specialized designs like high-torque motors.
-
DC Motors: DC motors generally provide higher starting torque, allowing them to accelerate heavy loads efficiently.
Efficiency:
-
AC Motors: AC motors, especially induction motors, are generally highly efficient, particularly at their rated load. Efficiency can be improved further by using high-efficiency motors and advanced control techniques.
-
DC Motors: DC motors can be highly efficient as well, especially brushless DC motors which surpass brushed DC motors and often compete with induction motors in terms of efficiency.
Maintenance:
-
AC Motors: AC motors, particularly induction motors, require minimal maintenance, often just periodic lubrication.
-
DC Motors: Brushed DC motors require regular brush replacement, adding to their maintenance needs. Brushless DC motors have significantly reduced maintenance requirements.
Cost:
-
AC Motors: AC motors are often less expensive than comparable DC motors, especially induction motors.
-
DC Motors: DC motors can be more expensive, particularly brushless DC motors, due to their more complex electronic control systems.
Applications: Where Each Motor Excels
The choice between AC and DC motors depends heavily on the specific application.
AC Motor Applications:
AC motors, particularly induction motors, dominate industrial applications due to their robustness, low cost, and high efficiency:
- Industrial Fans and Pumps: Their high efficiency and reliability make them ideal for continuous operation.
- Conveyors and Material Handling: Their robust construction and ability to handle heavy loads are key advantages.
- Compressors and HVAC Systems: Their high efficiency and relatively simple control contribute to their widespread use.
- Household Appliances: Many household appliances, such as refrigerators and washing machines, employ AC motors.
DC Motor Applications:
DC motors, particularly brushless DC motors, find applications where precise control and high performance are crucial:
- Robotics and Automation: Their precise speed and torque control are essential for accurate movements.
- Electric Vehicles: Brushless DC motors are common in electric vehicles due to their high efficiency and power density.
- Computer Peripherals: Hard drives and other computer peripherals often use DC motors.
- Medical Equipment: Precise control and reliability are paramount in medical applications.
- Power Tools: Many power tools benefit from the high torque and speed control offered by DC motors.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Motor
The decision of whether to use an AC or DC motor depends on a careful evaluation of the application requirements. Consider factors such as:
-
Required speed and torque characteristics: DC motors excel in applications demanding precise speed control and high starting torque, while AC motors are suitable for applications requiring consistent speed at high efficiency.
-
Cost considerations: AC motors generally offer a lower initial cost.
-
Maintenance requirements: AC motors typically require less maintenance.
-
Control complexity: DC motors can be easier to control for precise speed adjustments.
-
Environmental factors: The operating environment might influence the choice; some motors are better suited for harsh conditions.
By carefully weighing these factors, you can select the optimal motor type for your specific needs, ensuring efficient, reliable, and cost-effective operation. Understanding the fundamental differences and characteristics of AC and DC motors empowers you to make the best decision for your project.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are All The Factors Of 6
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Protons Does Potassium Have
Mar 19, 2025
-
Homogeneous Mixtures Are Also Known As
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Are The Multiples Of 50
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Hydrologic Cycle Is Driven By Energy From The
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Difference In Ac And Dc Motor . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
