Difference Between Baking Soda And Baking Powder Chemical Formula
Juapaving
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
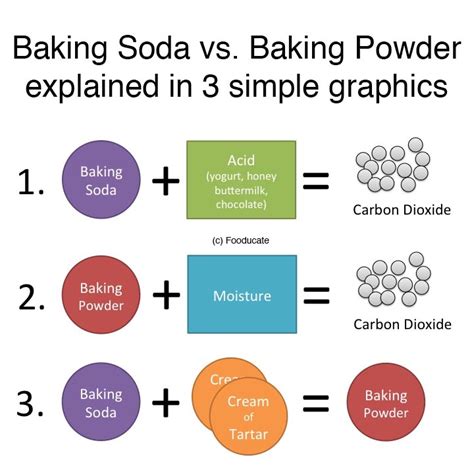
Table of Contents
Baking Soda vs. Baking Powder: A Deep Dive into Chemical Composition and Baking Magic
Baking enthusiasts often find themselves reaching for baking soda and baking powder, sometimes interchangeably, assuming they perform the same function. While both are leavening agents, crucial for creating light and airy baked goods, their chemical compositions and functionalities differ significantly. Understanding these differences is key to achieving consistent and successful baking results. This article will delve into the chemical formulas of baking soda and baking powder, explore their unique properties, and explain how to use them effectively.
The Chemical Formula Showdown: Baking Soda vs. Baking Powder
Let's start with the basics: the chemical formulas. This forms the bedrock of understanding their contrasting roles in baking.
Baking Soda: The Simple Alkali
Baking soda, also known as sodium bicarbonate, boasts a straightforward chemical formula: NaHCO₃. This signifies a single molecule comprising one sodium atom (Na), one hydrogen atom (H), one carbon atom (C), and three oxygen atoms (O). Its simplicity belies its potent leavening power. However, it's important to note that baking soda alone doesn't rise; it requires an acidic ingredient to activate its leavening properties.
How Baking Soda Works: Baking soda's leavening action relies on a chemical reaction with an acid. When exposed to heat and an acid (like buttermilk, lemon juice, vinegar, or even the acidic components in cocoa powder), it undergoes a decomposition reaction. This reaction releases carbon dioxide (CO₂), the gas responsible for the rise in baked goods. The equation looks something like this (using vinegar, acetic acid, as an example):
NaHCO₃ + CH₃COOH → CH₃COONa + H₂O + CO₂
This translates to: Sodium bicarbonate + Acetic acid → Sodium acetate + Water + Carbon dioxide.
This reaction is relatively fast, making baking soda ideal for recipes that require quick leavening and a light, airy texture.
Baking Powder: The Double-Acting Dynamo
Baking powder, on the other hand, is a more complex leavening agent. It's a mixture, not a single compound. Its composition typically includes baking soda (NaHCO₃) and one or more acid salts. Common acid salts include monocalcium phosphate (Ca(H₂PO₄)₂) and sodium aluminum sulfate (NaAl(SO₄)₂). These acid salts react with the baking soda in two stages:
-
First Reaction (Fast-Acting): Some of the acid salt reacts with the baking soda immediately upon mixing with wet ingredients. This produces a small amount of carbon dioxide, ensuring some initial leavening.
-
Second Reaction (Slow-Acting): The remaining acid salt reacts with the baking soda when exposed to the heat of the oven. This second reaction generates a larger volume of carbon dioxide, providing a second rise during baking.
This double-acting nature makes baking powder a versatile leavening agent suitable for a wider range of baking applications. The exact chemical reactions are more complex and depend on the specific acid salts used in the baking powder. However, the overall effect is the release of carbon dioxide gas in two phases.
Why the Double-Action is Crucial: The double-acting characteristic of baking powder is what sets it apart from baking soda. It allows for consistent leavening even if the batter sits for a while before baking, whereas baking soda’s reaction is more immediate and less forgiving of delays.
Understanding the Differences: A Practical Perspective
The chemical differences between baking soda and baking powder translate into significant functional distinctions in baking:
Requirement for Acid: A Key Distinguishing Feature
Baking soda requires an acidic ingredient to activate. Without it, it will not leaven properly. The lack of leavening will result in dense, flat baked goods. Recipes using baking soda often include ingredients such as buttermilk, yogurt, lemon juice, vinegar, or molasses to provide the necessary acidity.
Baking powder, however, is self-acting. It contains both the alkaline component (baking soda) and the acidic component. Therefore, it doesn't necessitate the addition of separate acidic ingredients.
The Timing Factor: Immediate vs. Delayed Leavening
Baking soda's leavening is immediate upon mixing with acidic ingredients and heat. This makes it ideal for quick breads and recipes where rapid leavening is desired.
Baking powder, with its double-acting nature, offers both an immediate and a delayed leavening action. This flexibility makes it suitable for cakes, cookies, and other recipes that can benefit from a slower, more controlled rise.
Taste and Aftertaste: A Subtle but Noticeable Difference
While both baking soda and baking powder are generally flavor-neutral, excessive baking soda can sometimes leave a slightly bitter or soapy aftertaste. This usually occurs when the ratio of acid to baking soda is unbalanced. Using the correct amount and ensuring adequate acid is present helps prevent this issue. Baking powder, on the other hand, is less likely to cause this issue, thanks to its balanced formulation.
Shelf Life: Storage and Stability
Baking soda tends to have a longer shelf life when stored properly in a cool, dry place. However, its effectiveness can be reduced over time, especially if exposed to moisture.
Baking powder's shelf life is generally shorter than baking soda's. The acid and alkaline components can react prematurely, reducing its leavening power. It’s advisable to check the expiration date printed on baking powder containers.
Choosing the Right Leavening Agent: A Baker's Guide
The choice between baking soda and baking powder depends entirely on the recipe and its specific requirements:
-
Recipes Requiring Baking Soda: Quick breads, muffins, some cookies, and recipes that specifically call for an acidic ingredient for flavor and leavening.
-
Recipes Requiring Baking Powder: Cakes, biscuits, scones, some cookies, and recipes where a more controlled and gradual rise is needed.
Important Note: Some recipes call for both baking soda and baking powder. This combination often enhances the overall leavening and texture. In such cases, understanding the roles of each leavening agent is vital for achieving optimal results.
Beyond the Basics: Troubleshooting Baking Issues
Sometimes, even with careful ingredient selection, baking can go wrong. Understanding the role of baking soda and baking powder can help troubleshoot common problems:
-
Flat Baked Goods: This could indicate insufficient leavening. Check your recipe to ensure the correct amount of baking powder or baking soda is used, and that sufficient acidic ingredients are present if using baking soda.
-
Bitter or Soapy Taste: This often points to too much baking soda relative to the acidic ingredients.
-
Uneven Rise: This can be due to uneven distribution of leavening agents in the batter or variations in oven temperature.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Leavening
Baking soda and baking powder, while both leavening agents, differ significantly in their chemical compositions and functionalities. Understanding their distinct properties, the chemical reactions involved, and the factors that influence their effectiveness empowers bakers to create a wide array of light, airy, and delicious baked goods. By understanding the nuances of each leavening agent, bakers can confidently tackle any recipe, mastering the art of achieving perfectly risen delights. Remember, consistent success in baking often comes down to mastering the fundamentals—and understanding the chemistry behind the magic is a significant step in that direction.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Cranial Bone
Apr 05, 2025
-
Eclipses Do Not Occur Every Month Because The Moons
Apr 05, 2025
-
Do Lipids Store More Energy Than Carbohydrates
Apr 05, 2025
-
Difference Between Real Numbers And Natural Numbers
Apr 05, 2025
-
What Does Vitamin A B C And D Do
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Difference Between Baking Soda And Baking Powder Chemical Formula . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
