Difference Between An Alternator And A Generator
Juapaving
Apr 06, 2025 · 6 min read
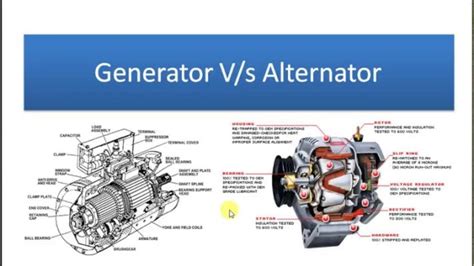
Table of Contents
Alternator vs. Generator: Unveiling the Key Differences
Understanding the difference between an alternator and a generator is crucial, especially for those interested in automobiles, power generation, or electrical engineering. While both devices convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, their underlying principles, designs, and applications differ significantly. This comprehensive guide will delve into the core distinctions between alternators and generators, clarifying their functionalities and highlighting their specific use cases.
Fundamental Differences: AC vs. DC Output
The most fundamental difference lies in their output: alternators produce alternating current (AC), while generators typically produce direct current (DC). This seemingly simple distinction has profound implications for their design, application, and associated components.
Alternators: The AC Powerhouses
Alternators utilize the principle of electromagnetic induction to generate AC electricity. A rotating magnetic field, created by the rotor, induces an alternating current in the stationary stator windings. This alternating current is then typically rectified to direct current using diodes before being used to power vehicle systems or other applications.
- Rotating magnetic field: The rotor is the rotating component, usually incorporating permanent magnets or electromagnets. Its rotation generates the changing magnetic field.
- Stationary stator: The stator is the stationary component containing windings of copper wire. The changing magnetic field from the rotor induces voltage in these windings.
- Rectifiers: Most automotive alternators incorporate diodes to convert the AC output to DC, suitable for powering car batteries and electrical systems.
- Higher efficiency: Alternators generally exhibit higher efficiency compared to DC generators, especially at higher speeds.
Generators: The DC Power Pioneers
DC generators, on the other hand, directly produce direct current. Their design involves a commutator, a rotating switch that converts the alternating current induced in the armature windings into a unidirectional (direct) current.
- Armature windings: These windings are typically located on the rotor and cut through the magnetic field lines produced by the stationary field magnets.
- Commutator: The commutator is a crucial component, consisting of segmented copper rings that reverse the current direction in the external circuit, resulting in a direct current output.
- Brushes: Carbon brushes make contact with the rotating commutator to deliver the DC electricity to the external circuit.
- Lower efficiency at higher speeds: DC generators tend to be less efficient than alternators, especially when operating at higher speeds. Their efficiency often decreases at higher speeds due to increased losses from friction and sparking at the commutator.
Applications: Where Each Shines
The differing output characteristics directly influence the applications of alternators and generators.
Alternators: The Automotive Workhorse and Beyond
Alternators are ubiquitous in automobiles, serving as the primary source of electrical power. Their ability to produce AC, easily rectified to DC, makes them ideal for charging the battery and powering various vehicle systems. Beyond automobiles, they find applications in:
- Power generation: Smaller, portable generators often employ alternators for their efficiency and ability to produce higher voltages.
- Industrial settings: Alternators are used in various industrial applications where AC power is required, like supplying power to machinery and equipment.
- Renewable energy: Wind turbines and some solar power systems use alternators to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Generators: Specialized Applications and Niche Markets
While less prevalent in everyday applications compared to alternators, DC generators still hold their place in specific niches. Their direct current output is crucial for:
- Electroplating: DC generators are often employed in electroplating processes requiring a stable, unidirectional current.
- Battery charging (specialized): Some specialized battery charging systems require DC generators, especially for older or high-capacity batteries.
- Specialized instruments: Certain scientific and measuring instruments might utilize DC generators for their stable, low-noise output.
- Small-scale power generation: Small-scale, low-power applications may use DC generators due to their simpler design in some instances.
Construction and Maintenance: A Comparative Overview
The construction and maintenance requirements of alternators and generators differ significantly due to their fundamental design differences.
Alternators: Simpler Construction, Easier Maintenance
The relatively simple construction of alternators contributes to their ease of maintenance and repair. The absence of a commutator and brushes minimizes wear and tear, extending their lifespan. Regular checks for belt tension and diode function are generally sufficient for maintaining an alternator.
Generators: More Complex Construction, More Involved Maintenance
DC generators possess a more complex construction involving the commutator and brushes. These components are prone to wear and tear, requiring periodic replacement. Maintenance includes regular brush inspection, commutator cleaning, and lubrication of bearings. The complexity adds to the cost of maintenance and the potential for downtime.
Efficiency and Performance: A Detailed Comparison
Both alternators and generators exhibit varying levels of efficiency based on factors such as design, load, and operating speed. However, a general trend shows alternators to be more efficient overall, especially at higher speeds.
Alternator Efficiency: Higher and More Consistent
Alternators generally boast higher efficiency across a broader range of operating speeds. The absence of mechanical switching in the commutator minimizes energy losses from friction and sparking. This higher efficiency translates into less wasted energy and a longer operational lifespan.
Generator Efficiency: Lower and More Variable
DC generators tend to exhibit lower efficiency compared to alternators, especially at higher speeds. The commutator and brushes contribute significantly to energy losses through friction and sparking. Efficiency also tends to fluctuate more significantly with changes in load and operating speed.
Cost Considerations: Balancing Performance and Budget
The cost of an alternator versus a generator can vary depending on factors like size, power output, and features. However, alternators generally tend to be less expensive to manufacture and purchase due to their simpler design.
Alternator Cost: Generally Lower
The simpler design of alternators usually leads to lower manufacturing costs. This translates into lower prices for consumers, making them a more cost-effective option for most applications.
Generator Cost: Potentially Higher
DC generators can be more expensive than alternators, especially for higher power outputs, due to the more complex construction involving the commutator, brushes, and other components. The higher maintenance costs also need to be considered when evaluating the overall cost of ownership.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Power Solution
The choice between an alternator and a generator ultimately depends on the specific application and its requirements. For automotive applications and many industrial settings where high efficiency and ease of maintenance are crucial, alternators are the clear winner. DC generators, while less common, retain their niche in specialized applications where direct current is essential and higher maintenance isn't a major concern. Understanding the fundamental differences outlined in this guide enables informed decision-making when selecting the appropriate power generation solution for any given scenario. The distinctions between AC and DC output, along with the implications for design, efficiency, and maintenance, are critical factors to consider.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Can A Compound Be Separated By Physical Means
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Is The Melting Point Of Ice
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 48 And 32
Apr 07, 2025
-
5 Letter Word With A And S
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Is Dispersion Of Light In Physics
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Difference Between An Alternator And A Generator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
