Compare And Contrast Hinduism And Buddhism
Juapaving
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
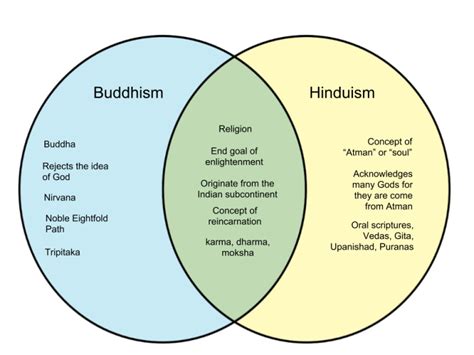
Table of Contents
Hinduism and Buddhism: A Comparison of Two Ancient Spiritual Traditions
Hinduism and Buddhism, two of the world's oldest and most influential religions, share a deep historical connection and a number of common philosophical threads. Yet, they also diverge significantly in their doctrines, practices, and ultimate goals. Understanding these similarities and differences provides invaluable insight into the rich tapestry of human spiritual experience. This comprehensive comparison will explore their core beliefs, rituals, and social impact.
Shared Roots and Common Ground
Both Hinduism and Buddhism originated in the Indian subcontinent. Buddhism, in fact, emerged as a reaction and reformulation of certain aspects of Hinduism. This shared origin explains the considerable overlap in their beliefs, particularly in their early stages. Several key similarities bind these two seemingly disparate traditions:
1. The Concept of Karma and Rebirth:
Both religions embrace the concept of karma, the principle of cause and effect, where actions have consequences that extend beyond this life. Good deeds lead to positive outcomes in future lives, while negative actions result in suffering. This belief underpins the idea of rebirth or samsara, the cyclical process of death and rebirth, a continuous cycle of suffering until liberation is achieved. The goal in both traditions is to escape this endless cycle.
2. The Importance of Meditation and Mindfulness:
Meditation plays a crucial role in both Hinduism and Buddhism. In Hinduism, various forms of meditation, like dhyana, are used to connect with the divine and achieve self-realization. Buddhism emphasizes mindfulness meditation (vipassana) and other practices to cultivate awareness, understanding the impermanent nature of reality, and achieving enlightenment. Both traditions recognize the power of introspection and mental discipline in attaining spiritual growth.
3. The Pursuit of Liberation (Moksha/Nirvana):
Both Hinduism and Buddhism aim for liberation from the cycle of birth and death. In Hinduism, this liberation is known as moksha, a state of union with the ultimate reality (Brahman). Buddhism seeks nirvana, a state of freedom from suffering and the illusion of self. While the paths to liberation differ, the ultimate goal of transcending suffering and achieving a state of peace is a shared aspiration.
4. The Importance of Dharma:
While interpreted differently, the concept of dharma is central to both. In Hinduism, dharma refers to the righteous conduct and duty appropriate to one's caste and stage of life. In Buddhism, dharma encompasses the Buddha's teachings and the path to enlightenment. Both emphasize ethical conduct and living a life aligned with principles of compassion, non-violence, and truthfulness as crucial steps towards spiritual progress.
Divergent Paths: Key Differences
Despite their shared heritage, Hinduism and Buddhism diverge significantly in their theological frameworks, practices, and ultimate goals:
1. The Nature of Reality:
Hinduism presents a complex cosmology with a multitude of gods and goddesses, considered different manifestations of a single ultimate reality, Brahman. This ultimate reality is seen as eternal, unchanging, and transcendent. The world is perceived as an illusion (Maya) that obscures the true nature of reality. The goal is to realize one's oneness with Brahman.
Buddhism, on the other hand, is generally considered non-theistic. While some schools acknowledge deities, the focus is not on worshiping them. The central emphasis is on understanding the nature of suffering and overcoming it through the path of the Buddha's teachings. The concept of a creator god is largely irrelevant. Reality is viewed as impermanent, constantly changing, and without inherent self (anatman).
2. The Concept of the Self (Atman/Anatman):
A crucial difference lies in the concept of self. Hinduism posits the existence of an eternal soul or self, Atman, which is ultimately identical to Brahman. The goal of spiritual practice is to realize this identity.
Buddhism, in contrast, denies the existence of a permanent, independent self, asserting the doctrine of Anatman. The self is viewed as a collection of constantly changing physical and mental processes. The illusion of a fixed self is a major source of suffering.
3. The Path to Liberation:
The paths to liberation differ considerably. Hinduism offers diverse paths (margas) to moksha, including the path of knowledge (jnana marga), the path of devotion (bhakti marga), and the path of action (karma marga). These paths emphasize different approaches to spiritual growth, depending on individual temperament and inclination.
Buddhism outlines the Eightfold Path, a practical guide to overcoming suffering and achieving nirvana. This path comprises eight interconnected elements: right understanding, right thought, right speech, right action, right livelihood, right effort, right mindfulness, and right concentration. It emphasizes ethical conduct, mental discipline, and wisdom.
4. Ritual and Practice:
Hinduism is characterized by a rich tapestry of rituals, ceremonies, and practices, varying widely across different sects and regions. These include temple worship, offerings to deities, sacred texts recitation, and various yogic practices. The caste system, although officially abolished in many countries, historically played a significant role in structuring social life and religious practice.
Buddhism, while encompassing diverse practices, generally emphasizes meditation, mindfulness, and ethical conduct. Rituals tend to be simpler, focusing on chanting, meditation, and acts of compassion. The monastic tradition plays a significant role, with monks and nuns dedicating their lives to spiritual practice. The caste system is explicitly rejected in Buddhism.
5. Scripture and Canon:
Hinduism has a vast and diverse body of scriptures, including the Vedas, Upanishads, Bhagavad Gita, and numerous other texts, accumulated over millennia. This vast collection reflects the evolution and diversification of Hindu thought.
Buddhism's canonical texts, known as the Tripitaka (three baskets), were compiled after the Buddha's death, containing his teachings and accounts of his life. Different schools of Buddhism have their own additional scriptures and commentaries.
Social Impact and Modern Relevance
Both Hinduism and Buddhism have had profound and lasting impacts on societies worldwide. Hinduism has shaped the cultural landscape of India and influenced neighbouring regions, impacting art, literature, music, and social structures. Its emphasis on dharma and karma has had a significant ethical influence.
Buddhism, after spreading beyond India, profoundly impacted societies in East and Southeast Asia, shaping the cultural, philosophical, and artistic traditions of countries like China, Japan, Korea, Tibet, and many others. Its emphasis on compassion, non-violence, and mindfulness continues to resonate with people across the globe.
In the modern world, both traditions face challenges and adaptations. Secularization and globalization have impacted their practices and relevance. Yet, both continue to attract followers, offering pathways to spiritual growth, ethical living, and finding meaning in a complex world. Their emphasis on inner peace, compassion, and mindful living remains valuable in navigating the stresses and complexities of modern life. The enduring appeal of both Hinduism and Buddhism lies in their capacity to address fundamental human questions about existence, suffering, and the path to liberation. Their continued evolution and adaptation ensure their relevance for generations to come. Understanding their similarities and differences is essential for appreciating the rich tapestry of human spiritual experience and the enduring power of these ancient traditions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5 Letter Words Start With A D
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is The Smallest Particle Of An Element
Apr 02, 2025
-
Electron Microscope Advantages Over Light Microscope
Apr 02, 2025
-
Hc Verma Part 1 Table Of Contents
Apr 02, 2025
-
Common Multiples Of 2 And 5
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Compare And Contrast Hinduism And Buddhism . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
