Common Denominator Of 7 And 9
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
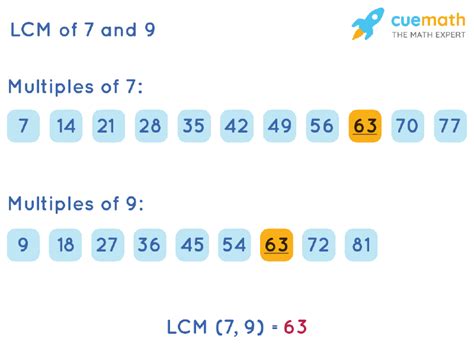
Table of Contents
Finding the Common Denominator of 7 and 9: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the common denominator of two numbers might seem like a simple task, especially for seemingly straightforward numbers like 7 and 9. However, understanding the underlying principles reveals a fascinating glimpse into number theory, a branch of mathematics exploring the properties of numbers. This article will delve into the process of finding the common denominator of 7 and 9, exploring various methods and expanding upon the broader mathematical concepts involved.
Understanding Common Denominators
Before we tackle the specific case of 7 and 9, let's clarify what a common denominator is. When dealing with fractions, a common denominator is a number that is a multiple of both denominators. It allows us to add, subtract, compare, and otherwise manipulate fractions efficiently. The least common denominator (LCD) is the smallest such number. This is particularly crucial for simplifying calculations and obtaining the most concise result.
Why We Need Common Denominators
Imagine trying to add 1/7 and 1/9 directly. You can't simply add the numerators because the fractions represent different parts of a whole. A common denominator provides a consistent unit of measurement, allowing for accurate addition or subtraction. Without it, the result would be nonsensical.
Methods for Finding the Least Common Denominator (LCD) of 7 and 9
Several methods exist to determine the LCD of 7 and 9. Let's explore the most common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples
The most straightforward method is listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found.
- Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70…
- Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72…
Notice that 63 appears in both lists. Therefore, 63 is a common multiple of 7 and 9. In fact, it's the least common multiple (LCM), as it's the smallest number that appears in both lists. Since the LCD of two numbers is equal to their LCM, the LCD of 7 and 9 is 63.
2. Prime Factorization
This method utilizes the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers. Let's break down 7 and 9 into their prime factors:
- 7: 7 (7 is a prime number)
- 9: 3 x 3 = 3²
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorization of either number:
- The highest power of 3 is 3².
- The highest power of 7 is 7.
Therefore, the LCM (and hence the LCD) is 3² x 7 = 9 x 7 = 63.
This method is particularly efficient for larger numbers, as it avoids the potentially lengthy process of listing multiples.
3. Using the Formula: LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
This method leverages the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the two numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. For 7 and 9, the GCD is 1, as they share no common factors other than 1. They are relatively prime.
Applying the formula:
LCM(7, 9) = (|7 x 9|) / GCD(7, 9) = 63 / 1 = 63
This method elegantly connects the LCM and GCD, providing an alternative approach to finding the LCD.
The Significance of Relatively Prime Numbers
The numbers 7 and 9 are examples of relatively prime numbers (also known as coprime numbers). This means their greatest common divisor (GCD) is 1. In such cases, the LCM (and therefore the LCD) is simply the product of the two numbers. This is a noteworthy simplification when dealing with relatively prime numbers.
Applications of Common Denominators
Understanding common denominators is crucial in various mathematical contexts:
1. Fraction Arithmetic
As mentioned earlier, common denominators are essential for adding, subtracting, and comparing fractions. Without them, performing these operations accurately is impossible.
2. Solving Equations
Common denominators often simplify equations involving fractions, making them easier to solve. This is particularly relevant in algebra and calculus.
3. Ratio and Proportion Problems
Many real-world problems involve ratios and proportions, which frequently require the use of common denominators for accurate calculations and comparisons.
4. Measurement and Units Conversion
Common denominators play a vital role in converting between different units of measurement, ensuring consistent comparisons and calculations.
Extending the Concept: More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCD of more than two numbers. For instance, to find the LCD of 7, 9, and another number, say 12, you would still employ the prime factorization method or variations of the LCM calculation. You would identify the highest power of each prime factor appearing in the prime factorization of any of the numbers and then multiply these highest powers together.
Conclusion: The Common Denominator and Beyond
While finding the common denominator of 7 and 9 might seem a straightforward exercise, it provides a valuable gateway to understanding fundamental concepts in number theory, including prime factorization, the relationship between LCM and GCD, and the significance of relatively prime numbers. The techniques discussed here extend far beyond this simple example, forming a foundation for more complex mathematical operations and applications across various fields. Mastering these concepts significantly enhances problem-solving abilities and deepens one's appreciation for the elegance and interconnectedness of mathematics. Remember, understanding the 'why' behind the mathematical procedures is just as important, if not more so, than simply obtaining the correct answer.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Size Chart In Cm And Inches
May 09, 2025
-
How Heat Is Different From Temperature
May 09, 2025
-
Where Are Calcium Ions Stored In The Muscle Cell
May 09, 2025
-
The Neutral Particle In The Nucleus Of An Atom
May 09, 2025
-
Label The Structures Of The Vertebrae
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Denominator Of 7 And 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.