Check All Equations That Are Equivalent.
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
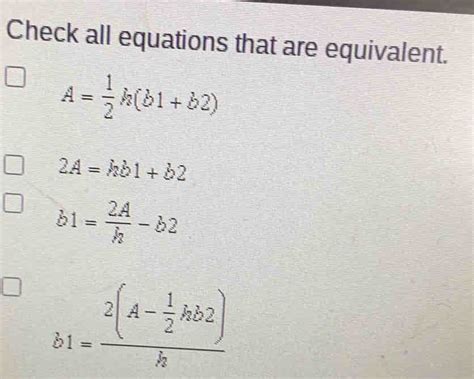
Table of Contents
Checking for Equivalent Equations: A Comprehensive Guide
Equivalent equations are mathematical statements that have the same solution set. This means that any value of the variable that satisfies one equation will also satisfy the other, and vice versa. Identifying equivalent equations is crucial in algebra and beyond, allowing for simplification of problems, manipulation of formulas, and a deeper understanding of mathematical relationships. This comprehensive guide will explore various techniques and examples to help you master the art of recognizing equivalent equations.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What Makes Equations Equivalent?
Before diving into specific techniques, it's crucial to grasp the underlying principles. Two equations are equivalent if and only if they have the same solution set. This means that any value that makes one equation true will also make the other equation true, and vice versa. No solutions are gained or lost in the transformation between equivalent equations.
Key Operations Preserving Equivalence:
Several operations, when applied correctly, guarantee the resulting equation is equivalent to the original. These include:
-
Adding or Subtracting the Same Quantity: Adding or subtracting the same term to both sides of an equation maintains equivalence. For example, x + 2 = 5 is equivalent to x + 2 - 2 = 5 - 2, which simplifies to x = 3.
-
Multiplying or Dividing by the Same Non-Zero Quantity: Multiplying or dividing both sides of an equation by the same non-zero number also preserves equivalence. For instance, 2x = 6 is equivalent to (2x)/2 = 6/2, which simplifies to x = 3. Important Note: Dividing by zero is undefined and will invalidate the equivalence.
-
Simplifying Expressions: Combining like terms, expanding brackets, or factoring expressions correctly will result in an equivalent equation. For example, 3x + 2x + 5 = 15 is equivalent to 5x + 5 = 15.
Methods for Checking Equation Equivalence
Let's explore several practical methods for determining if two or more equations are equivalent.
1. Solving the Equations
The most straightforward approach is to solve each equation individually and compare their solution sets. If the solution sets are identical, the equations are equivalent.
Example:
Are x + 5 = 8 and 2x - 1 = 11 equivalent?
- Solve x + 5 = 8: Subtract 5 from both sides: x = 3
- Solve 2x - 1 = 11: Add 1 to both sides: 2x = 12. Divide both sides by 2: x = 6
Since the solution sets are {3} and {6}, respectively, these equations are not equivalent.
2. Manipulating One Equation to Obtain the Other
This method involves performing valid algebraic operations on one equation to see if it can be transformed into the other. If this transformation is possible using only the operations that preserve equivalence (as listed above), the equations are equivalent.
Example:
Are 3x + 6 = 15 and x + 2 = 5 equivalent?
Let's start with 3x + 6 = 15:
- Subtract 6 from both sides: 3x = 9
- Divide both sides by 3: x = 3
Now let's work with x + 2 = 5:
- Subtract 2 from both sides: x = 3
Both equations lead to the solution x = 3. Therefore, they are equivalent.
3. Graphical Comparison (For Linear Equations)
For linear equations (equations of the form ax + b = c), a graphical comparison can be useful. If the graphs of the equations are identical, the equations are equivalent. This method is particularly helpful in visualizing the relationship between the equations. Remember that both equations must have the same solution set, i.e., intersect the x-axis at the same point.
4. Substitution Method
This method involves substituting the solution of one equation into the other equation. If the substituted solution satisfies the second equation, the equations are equivalent. This technique is especially helpful when dealing with systems of equations or equations involving multiple variables.
Example:
Are 2x + y = 5 and y = 5 - 2x equivalent?
Let's solve 2x + y = 5 for y:
y = 5 - 2x
This shows that both equations can be transformed to the same form, therefore, they are equivalent.
Advanced Cases and Considerations
While the above methods cover many scenarios, some situations require a more nuanced approach.
Equations with No Solutions or Infinitely Many Solutions
Some equations have no solutions (inconsistent equations) or infinitely many solutions (dependent equations). Equivalent equations will always share the same solution characteristic. If one equation has no solution, any equivalent equation will also have no solution. Similarly, if one equation has infinitely many solutions, any equivalent equation will also have infinitely many solutions.
Example:
- x + 2 = x + 3 (no solution)
- 2x + 4 = 2(x + 2) (infinitely many solutions)
Non-Linear Equations
Checking equivalence for non-linear equations (equations that involve higher powers of the variable, like quadratic equations or trigonometric equations) can be more challenging. The same principles apply: the solution sets must be identical. Solving these equations might require more advanced techniques like factoring, the quadratic formula, or numerical methods.
Systems of Equations
When dealing with systems of equations, equivalence means that the systems have the same solution set. Equivalent systems can be obtained through operations such as adding or subtracting equations, multiplying an equation by a constant, or substituting one equation into another. Gaussian elimination and other matrix methods are commonly used to determine equivalence in systems of linear equations.
Practical Applications of Equivalent Equations
Understanding equivalent equations is not just a theoretical exercise; it has significant practical applications across various fields:
-
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions: Transforming complex equations into simpler, equivalent forms makes solving them much easier.
-
Solving Equations: The ability to manipulate equations while maintaining equivalence is essential for solving for unknown variables.
-
Formula Manipulation: In physics, engineering, and other sciences, manipulating formulas to solve for a specific variable often involves transforming the equation into an equivalent form.
-
Computer Programming: Equivalent equations are used in computer algorithms and programs to perform calculations and solve problems efficiently.
-
Data Analysis: In statistics and data analysis, equivalent equations can be used to simplify calculations and derive insights from data.
Conclusion: Mastering Equation Equivalence
The ability to identify equivalent equations is a fundamental skill in mathematics and its applications. By mastering the techniques discussed in this guide, you'll be better equipped to simplify complex problems, solve equations efficiently, and deepen your understanding of mathematical relationships. Remember that the core principle underlying equation equivalence is the identity of their solution sets. Always verify that no solutions are gained or lost during any manipulation. Practice regularly with various equation types to build your proficiency and confidence in identifying equivalent equations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A Polygon With Seven Sides
Mar 13, 2025
-
Age Limit For Indian Civil Services
Mar 13, 2025
-
Slope As A Rate Of Change
Mar 13, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple 6 And 15
Mar 13, 2025
-
A Broom Is What Type Of Simple Machine
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Check All Equations That Are Equivalent. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
