Can Electric Potential Energy Be Negative
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
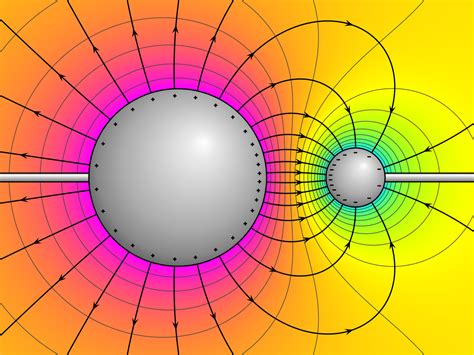
Table of Contents
Can Electric Potential Energy Be Negative?
The question of whether electric potential energy can be negative is a common one among students of physics. The answer, surprisingly, is yes. Understanding why requires a solid grasp of the concepts of electric potential energy, potential difference, and the reference point used for defining zero potential. This article will delve deep into these concepts, explaining not just if electric potential energy can be negative but also when and why.
Understanding Electric Potential Energy
Electric potential energy (EPE) is the energy a charged particle possesses due to its position in an electric field. Just like a mass has gravitational potential energy based on its height above the Earth, a charge has electric potential energy based on its location relative to other charges. This energy is a consequence of the electrostatic force between charges, which is either attractive (opposite charges) or repulsive (like charges).
The crucial point to remember is that electric potential energy is relative. It's not an absolute quantity but depends entirely on the choice of a reference point where the potential energy is defined as zero. This is analogous to gravitational potential energy; we often set the Earth's surface as the zero point, but we could equally choose sea level or even a point in space.
The Role of the Reference Point
The selection of a reference point is arbitrary but crucial. Changing the reference point will alter the absolute value of the EPE for every charge in the system, although the difference in potential energy between two points remains the same. This invariance of the potential difference is extremely important in practical applications.
Let's consider a simple example: two point charges, one positive and one negative. If we choose the reference point to be infinitely far away from both charges, then:
-
The positive charge will have positive electric potential energy. Work must be done against the repulsive force of the electric field to bring the positive charge from infinity to its current position near the negative charge. This work is stored as positive potential energy.
-
The negative charge will also have positive electric potential energy. Bringing the negative charge from infinity requires work against the attractive force of the electric field of the positive charge.
However, if we choose the reference point to be closer to the positive charge, the situation changes. The negative charge would now have a negative electric potential energy because its position is at a lower potential than the reference point. The positive charge, meanwhile, could have a positive or negative EPE depending on its distance from the reference point. This illustrates the relative nature of EPE.
Calculating Electric Potential Energy
The electric potential energy between two point charges q₁ and q₂ separated by a distance r is given by Coulomb's Law:
U = k * q₁ * q₂ / r
where k is Coulomb's constant (approximately 8.99 x 10⁹ N⋅m²/C²).
Notice that this equation gives a positive value when q₁ and q₂ have the same sign (both positive or both negative), representing a repulsive interaction, and a negative value when they have opposite signs (one positive and one negative), representing an attractive interaction. This directly reflects the sign of the potential energy.
Negative Potential Energy: A Deeper Dive
The negative sign in the equation when charges are oppositely signed doesn't imply a lack of energy. Instead, it indicates that the system is in a bound state. The charges are attracted to each other, and energy must be added to separate them. The negative potential energy represents the amount of work that would need to be done to completely separate the charges to infinity (where the potential energy is defined as zero).
This concept is analogous to the gravitational potential energy of a planet orbiting a star. The planet has negative gravitational potential energy, indicating that energy must be added to escape the star's gravitational pull. Similarly, energy needs to be added to overcome the attractive force between oppositely charged particles.
Electric Potential and Potential Difference
To further clarify the concept of negative potential energy, let's examine electric potential (V) and potential difference (ΔV).
Electric potential is defined as the electric potential energy per unit charge:
V = U / q
Potential difference, also known as voltage, is the difference in electric potential between two points. It's the work done per unit charge in moving a charge between those two points:
ΔV = V₂ - V₁ = (U₂ / q) - (U₁ / q)
Crucially, while the absolute value of potential can be positive or negative, potential difference is only concerned with the change in potential energy. Therefore, even if both points have negative potential, a positive potential difference could exist between them if one point has a higher (less negative) potential than the other.
Applications and Real-World Examples
The concept of negative electric potential energy is not merely theoretical; it has practical implications in numerous fields:
-
Atomic Physics: Electrons in an atom are bound to the nucleus by the attractive electrostatic force. Their electric potential energy is negative, representing the energy required to ionize the atom (remove the electron).
-
Chemistry: Chemical bonds are formed due to the attractive forces between atoms. The energy released during bond formation is related to the negative potential energy of the system.
-
Electronics: In electronic circuits, the reference point (ground) is arbitrarily set, and components will experience positive or negative voltages relative to this reference.
-
Nuclear Physics: The strong nuclear force binds protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus. This force can also be modeled using concepts similar to electric potential energy. Although significantly stronger and more complex, the principle of a system having negative potential energy is similar.
Conclusion: Embracing the Relativity of Electric Potential Energy
The ability of electric potential energy to be negative isn't a flaw in the model, but rather a fundamental consequence of its relative nature. The choice of a reference point determines whether the EPE is positive, negative, or zero. The critical aspect is not the absolute value but the potential difference between points, which determines the work done when moving charges within an electric field. Understanding this relativity, along with the implications for bound systems and real-world applications, is key to a comprehensive understanding of electrostatics. The negative sign simply signifies a bound state where energy is required to separate the interacting charges. Therefore, the question is not whether electric potential energy can be negative but under what conditions it will be. The answer lies in the arrangement and types of charges involved and the choice of reference point.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Found In Both Eukaryotic And Prokaryotic Cells
May 09, 2025
-
What Happens To Air As It Is Heated
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters Is 8 Millimeters
May 09, 2025
-
420 Degrees To Radians In Simplest Form
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Advantage Of Sexual Reproduction Over Asexual Reproduction
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Can Electric Potential Energy Be Negative . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.