Biuret Reagent Is Used To Test For The Presence Of
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
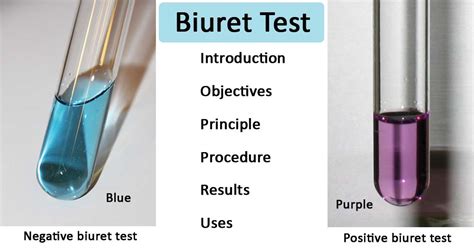
Table of Contents
Biuret Reagent: A Comprehensive Guide to Protein Detection
The Biuret test is a widely used chemical test for detecting the presence of peptide bonds. This means it's a highly effective method for identifying proteins, since proteins are essentially long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Understanding the Biuret reagent, its mechanism, applications, and limitations is crucial for various scientific disciplines, from biochemistry to clinical diagnostics. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the intricacies of this essential laboratory technique.
What is the Biuret Reagent?
The Biuret reagent is an alkaline solution of copper(II) sulfate, which is often combined with other ingredients such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide and potassium sodium tartrate. The key component is the copper(II) ion (Cu²⁺), which interacts specifically with peptide bonds. The addition of potassium sodium tartrate (Rochelle salt) acts as a chelating agent, preventing the precipitation of copper(II) hydroxide. This ensures a stable and effective reagent solution.
How Does the Biuret Test Work?
The Biuret test relies on the coordination complex formed between the copper(II) ions and the nitrogen atoms within peptide bonds. In an alkaline environment, the copper(II) ions form a coordination complex with the nitrogen atoms of the peptide bonds, resulting in a distinct color change. This color change is the basis for the detection.
The Mechanism:
-
Alkaline Conditions: The addition of a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH), creates an alkaline environment. This environment is essential for the deprotonation of the nitrogen atoms in the peptide bonds, making them available for coordination with the copper(II) ions.
-
Coordination Complex Formation: The copper(II) ions (Cu²⁺) from the copper(II) sulfate react with the deprotonated nitrogen atoms in peptide bonds. Each Cu²⁺ ion can coordinate with multiple peptide bonds, forming a complex with a characteristic violet or purple color. The intensity of this color is directly proportional to the concentration of peptide bonds present in the sample.
-
Color Change Indication: The formation of the copper-peptide complex results in a visible color change, typically from light blue (the color of the copper(II) sulfate solution) to a violet or purple color. The intensity of the purple color indicates the concentration of peptide bonds, and therefore, the concentration of protein in the sample. A faint pink color may indicate the presence of short peptides, while a more intense purple indicates higher concentrations of proteins with many peptide bonds.
Factors Affecting the Biuret Test
Several factors can influence the accuracy and reliability of the Biuret test results. These include:
1. Concentration of the Sample:
The intensity of the color change directly correlates with the concentration of peptide bonds. Higher protein concentrations yield a more intense purple color.
2. pH of the Solution:
Maintaining an alkaline pH is crucial for the successful execution of the Biuret test. The alkaline environment deprotonates the nitrogen atoms, enabling coordination with the copper(II) ions. Deviations from the optimal pH can result in inaccurate or no color change.
3. Presence of Interfering Substances:
Certain substances can interfere with the Biuret test, leading to false-positive or false-negative results. For instance, high concentrations of ammonium ions or reducing sugars can interfere with the reaction. Additionally, the presence of certain metal ions could lead to interference. Careful sample preparation is often necessary to minimize these effects.
4. Temperature:
The reaction rate of the Biuret test is temperature-dependent. Higher temperatures generally lead to a faster reaction, although extreme temperatures might affect the stability of the reagent. The optimal temperature for the Biuret test is typically room temperature.
Applications of the Biuret Test
The Biuret test finds extensive use in various fields, including:
1. Biochemistry and Clinical Diagnostics:
The primary application of the Biuret test is the quantitative determination of protein concentration in biological samples. This includes blood serum, urine, tissue extracts, and other biological fluids. It provides a relatively simple and inexpensive method for protein quantification.
2. Food Science:
The Biuret test is used in food science to determine the protein content in various food products. This information is important for nutritional labeling and quality control purposes.
3. Environmental Science:
The test may be used to assess protein levels in environmental samples, such as wastewater or soil extracts, to evaluate the impact of pollution or the presence of microbial activity.
4. Pharmaceutical Industry:
The Biuret test can be employed to monitor protein concentrations during pharmaceutical drug production and quality control.
Advantages of the Biuret Test
- Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness: The test is relatively simple to perform and requires inexpensive reagents. This makes it readily accessible for various applications.
- Specificity for Peptide Bonds: The test is relatively specific for peptide bonds, minimizing interference from other compounds.
- Quantitative Analysis: The intensity of the color change is proportional to the concentration of protein in the sample. This allows for quantitative determination of protein content using a spectrophotometer.
- Wide Applicability: The test can be used to analyze various types of samples, including biological fluids, food products, and environmental samples.
Limitations of the Biuret Test
Despite its numerous advantages, the Biuret test has some limitations:
- Sensitivity: The Biuret test is not highly sensitive. It cannot detect small quantities of protein. Therefore, it's less suitable for samples with very low protein concentrations.
- Interference: As mentioned previously, certain substances can interfere with the test, leading to inaccurate results. Careful sample preparation and control experiments are crucial.
- Not Suitable for All Proteins: Some proteins, especially those with unique structural features, may not react readily with the Biuret reagent.
- False Positives: While specific for peptide bonds, the Biuret test can occasionally produce false positives in the presence of certain compounds.
Comparison with other Protein Assays
Several other assays are used to determine protein concentration. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses, making the choice dependent on specific needs:
-
Bradford Assay: This assay uses Coomassie Brilliant Blue dye, which binds to proteins, producing a color change. It's more sensitive than the Biuret test but can be affected by different protein compositions.
-
Lowry Assay: This assay combines the Biuret reaction with the reduction of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. It offers greater sensitivity than the Biuret test but is more complex and has more potential for interference.
-
BCA Assay (Bicinchoninic Acid Assay): The BCA assay is another colorimetric assay using bicinchoninic acid, which forms a complex with copper ions. It is highly sensitive and less prone to interference compared to the Lowry assay.
Conclusion
The Biuret test remains a valuable tool for detecting and quantifying proteins in a variety of applications. While it has limitations in sensitivity and potential for interference, its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and relative specificity make it a widely used method in biochemistry, clinical diagnostics, and other related fields. Understanding the underlying mechanism, limitations, and potential interferences is crucial for accurate and reliable results. Choosing the appropriate protein assay often depends on factors such as sample characteristics, required sensitivity, and available resources. Researchers should carefully consider these factors when selecting a suitable method for protein quantification. Further advancements in protein assay methodologies continue to enhance both sensitivity and precision, offering more sophisticated techniques for the future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Select All Of The Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Cells
Mar 18, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 16 And 28
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is 35713 In Expanded Form
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Word That Starts With R And Ends With R
Mar 18, 2025
-
Can You Touch A Venus Fly Trap
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Biuret Reagent Is Used To Test For The Presence Of . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
