Are The Diagonals Of A Square Perpendicular
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
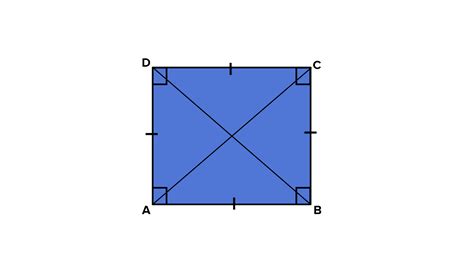
Table of Contents
Are the Diagonals of a Square Perpendicular? A Comprehensive Exploration
The question, "Are the diagonals of a square perpendicular?" might seem trivial at first glance. The answer, a resounding yes, is often intuitively grasped. However, a deeper dive into the geometry of squares reveals a fascinating interplay of properties that underpin this seemingly simple fact. This exploration will not only prove the perpendicularity of the diagonals but also delve into related concepts, demonstrating the rich mathematical tapestry woven within this seemingly simple geometric shape.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Squares and Their Properties
Before we delve into the proof, let's establish a strong foundation by defining a square and its key properties. A square is a quadrilateral (a four-sided polygon) characterized by the following:
- Four equal sides: All four sides of a square have the same length.
- Four right angles: Each of the four interior angles measures 90 degrees.
- Parallel opposite sides: Opposite sides of a square are parallel to each other.
These properties are crucial in understanding why the diagonals are perpendicular. The combination of equal sides and right angles creates a unique symmetry that leads to many interesting geometric relationships, including the perpendicularity of the diagonals.
Proving the Perpendicularity: Multiple Approaches
There are several ways to mathematically prove that the diagonals of a square are perpendicular. We'll explore two common approaches: using the properties of the square and employing vector algebra.
Method 1: Utilizing the Properties of a Square
This method relies directly on the defining characteristics of a square. Consider a square ABCD, with vertices A, B, C, and D. Let's draw the diagonals AC and BD, intersecting at point O.
-
Isosceles Triangles: The diagonals of a square bisect each other. This means that AO = OC and BO = OD. Furthermore, since all sides of the square are equal (AB = BC = CD = DA), triangles ABO, BCO, CDO, and DAO are all isosceles triangles.
-
Congruent Triangles: Notice that triangle ABO is congruent to triangle CDO (Side-Angle-Side congruence). Similarly, triangle BCO is congruent to triangle DAO. This congruence arises directly from the equal side lengths and the shared angles of the square.
-
Angle Relationships: Because triangles ABO and CDO are congruent, their corresponding angles are equal. Specifically, ∠AOB = ∠COD. Similarly, ∠BOA = ∠DOC. Since ∠AOB and ∠COD are vertically opposite angles, they are equal. The same holds true for ∠BOA and ∠DOC.
-
Sum of Angles: The angles around point O sum to 360 degrees. Therefore, ∠AOB + ∠BOC + ∠COD + ∠DOA = 360°. Since ∠AOB = ∠COD and ∠BOC = ∠DOA (due to congruent triangles and vertically opposite angles), we can simplify this to 2∠AOB + 2∠BOC = 360°. This simplifies to ∠AOB + ∠BOC = 180°.
-
Perpendicularity: Since the sum of angles ∠AOB and ∠BOC is 180°, this implies that the diagonals AC and BD are perpendicular to each other. The angles formed at their intersection (O) are all 90 degrees.
Method 2: Applying Vector Algebra
This method offers a more sophisticated approach using vector concepts. Let's represent the vertices of the square using vectors.
-
Vector Representation: Let's place the square on a coordinate plane. Let A be the origin (0, 0). Let vector a represent the vector from A to B, and vector b represent the vector from A to D. Since the sides are perpendicular, a and b are orthogonal (their dot product is zero: a • b = 0). Furthermore, |a| = |b| because the sides are of equal length.
-
Diagonal Vectors: The vector representing diagonal AC is a + b. The vector representing diagonal BD is b - a.
-
Dot Product and Perpendicularity: To determine if the diagonals are perpendicular, we calculate the dot product of the vectors representing the diagonals:
(a + b) • (b - a) = a • b - a • a + b • b - b • a
Since a • b = 0 (orthogonality), and a • a = |a|² and b • b = |b|², and |a| = |b|, the equation simplifies to:
0 - |a|² + |b|² - 0 = 0
This shows that the dot product of the diagonal vectors is zero. A dot product of zero indicates that the vectors are orthogonal, meaning the diagonals are perpendicular.
Beyond Perpendicularity: Further Implications
The perpendicularity of the diagonals is just one piece of the larger puzzle of a square's geometric properties. This fundamental property leads to several other significant consequences:
-
Equal Length Diagonals: The diagonals of a square are not only perpendicular but also have equal lengths. This stems from the Pythagorean theorem, easily applied to the right-angled triangles formed by the diagonals and the sides.
-
Area Calculation: The perpendicularity of the diagonals provides a convenient way to calculate the area of a square. The area can be calculated as half the product of the lengths of the diagonals.
-
Symmetry and Transformations: The perpendicularity contributes to the high degree of symmetry found in squares. Squares exhibit rotational symmetry of order 4 and reflectional symmetry across multiple axes.
-
Applications in other geometric shapes: Understanding the properties of squares, including the perpendicularity of their diagonals, is crucial in analyzing and understanding other geometric shapes, such as rhombuses (which share the property of perpendicular diagonals) and other quadrilaterals.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The concept of perpendicular diagonals in squares finds practical applications in various fields:
-
Architecture and Engineering: The square's properties, including perpendicular diagonals, are foundational in structural design and construction. Many buildings and structures utilize square or rectangular frameworks which rely on these geometric relationships for stability and strength.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: In computer graphics and game development, squares and their properties are used extensively to create and manipulate two-dimensional objects and scenes. The perpendicularity of the diagonals is essential for accurate calculations and rendering.
-
Cartography and Surveying: Squares and grids based on square principles are utilized in mapmaking and land surveying, ensuring accurate representation and measurements.
-
Art and Design: The visual appeal of squares and their symmetry are frequently employed in art and design to create balance and harmony. The relationship between diagonals and the overall structure contributes to the aesthetic quality.
Conclusion: A Simple Truth with Profound Implications
While the answer to "Are the diagonals of a square perpendicular?" appears straightforward, the journey to understanding this property reveals a wealth of mathematical concepts and their interconnectedness. From basic geometric principles to sophisticated vector algebra, the perpendicularity of the diagonals serves as a springboard to explore a broader understanding of squares and their significance in various disciplines. This seemingly simple geometric fact underlines the beauty and power of mathematical reasoning, showcasing how fundamental truths can have far-reaching consequences. The exploration highlights the importance of rigorous proof and the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts, reinforcing the elegance and utility of geometry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 60 Square Meters
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Formula Of A Hydronium Ion
May 09, 2025
-
Real Life Example Of A Right Angle
May 09, 2025
-
How To Multiply A 3x3 Matrix By A 3x1 Matrix
May 09, 2025
-
What X Value Makes The Set Of Ratios Equivalent
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Are The Diagonals Of A Square Perpendicular . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.