Are Acids Good Conductors Of Electricity
Juapaving
Apr 04, 2025 · 5 min read
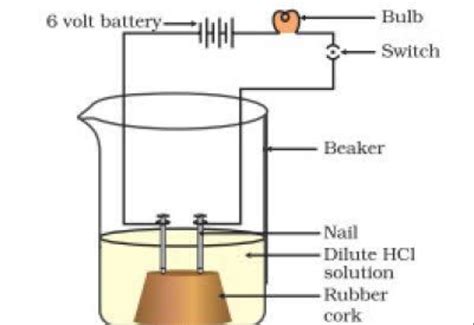
Table of Contents
Are Acids Good Conductors of Electricity? Exploring the Chemistry Behind Conductivity
Acids, a cornerstone of chemistry, are known for their sour taste and ability to react with bases. But beyond these familiar characteristics lies a fascinating property: their electrical conductivity. The question, "Are acids good conductors of electricity?" isn't a simple yes or no. The answer depends on several factors, primarily the concentration of the acid and its degree of ionization. This comprehensive exploration will delve into the intricate relationship between acids, ions, and electrical conductivity.
Understanding Electrical Conductivity
Before examining the conductivity of acids, let's establish a fundamental understanding of electrical conductivity itself. Electrical conductivity is the ability of a material to allow the flow of electric current. This flow is facilitated by the movement of charged particles, namely ions and electrons. In the context of solutions, such as acidic solutions, the conductivity is primarily determined by the presence and mobility of ions.
The Role of Ions
Ions are atoms or molecules that carry a net electrical charge. Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions. When an electric field is applied across a solution containing ions, these charged particles migrate towards the oppositely charged electrode. This movement of ions constitutes the electric current. The greater the number of ions and their mobility, the higher the conductivity.
Acids and Ionization: The Key to Conductivity
Acids are substances that donate protons (H⁺ ions) when dissolved in a solution. The extent to which an acid donates protons determines its strength and, consequently, its conductivity. This process is known as ionization or dissociation.
Strong Acids vs. Weak Acids
Strong acids, like hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), completely ionize in water. This means that virtually all of the acid molecules break apart into their constituent ions (H⁺ and the corresponding anion). This high concentration of mobile ions makes strong acids excellent conductors of electricity.
Weak acids, such as acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and carbonic acid (H₂CO₃), only partially ionize in water. A significant portion of the acid molecules remain undissociated, resulting in a lower concentration of ions compared to strong acids. Consequently, weak acids are weaker conductors of electricity than strong acids.
The Equilibrium Constant: A Measure of Ionization
The degree of ionization of a weak acid is quantified by its acid dissociation constant (Ka). Ka is an equilibrium constant that represents the ratio of the concentrations of the dissociated ions to the concentration of the undissociated acid molecules. A higher Ka value indicates a greater degree of ionization and, therefore, higher conductivity.
Factors Affecting the Conductivity of Acidic Solutions
Several factors influence the conductivity of acidic solutions beyond the inherent strength of the acid:
Concentration
The concentration of the acid directly impacts its conductivity. A higher concentration means more acid molecules are available to ionize, leading to a higher concentration of ions and improved conductivity. This relationship, however, isn't always linear. At extremely high concentrations, interionic attractions can hinder ion mobility, reducing conductivity.
Temperature
Temperature plays a crucial role in conductivity. Increasing the temperature increases the kinetic energy of the ions, allowing them to move more freely and rapidly through the solution. This increased mobility translates to higher conductivity.
Solvent
The nature of the solvent also affects conductivity. Water is a common solvent for acids, and its polarity facilitates the ionization process. However, other solvents with different dielectric constants can influence the extent of ionization and, therefore, the conductivity.
Presence of Impurities
The presence of impurities in the acidic solution can affect its conductivity. Impurities can introduce additional ions, increasing conductivity, or they might react with the acid, altering its ionization and affecting conductivity. Pure acid solutions generally exhibit higher conductivity than impure solutions.
Measuring the Conductivity of Acidic Solutions
The conductivity of acidic solutions is measured using a conductivity meter. This instrument measures the ability of a solution to conduct an electric current. The conductivity is typically expressed in Siemens per meter (S/m) or milliSiemens per centimeter (mS/cm). The higher the value, the better the conductivity.
Applications of Acidic Conductivity
The conductivity of acids finds applications in various fields:
Industrial Processes
Acidic solutions are used extensively in industrial processes where their conductivity is exploited. Examples include electroplating, where the conductivity of the electrolyte solution is crucial for efficient metal deposition, and battery technology, where the conductivity of the electrolyte determines the performance of the battery.
Analytical Chemistry
Conductivity measurements are employed in analytical chemistry to determine the concentration of acids and other ionic species in solutions. This technique is relatively simple, rapid, and inexpensive, making it a valuable tool for various analytical applications.
Environmental Monitoring
Conductivity measurements are also used in environmental monitoring to assess the quality of water resources. High conductivity can indicate the presence of dissolved salts and acids, potentially indicating pollution.
Conclusion: A nuanced relationship
The question "Are acids good conductors of electricity?" has a nuanced answer. Strong acids are excellent conductors because they completely ionize, producing high concentrations of mobile ions. Weak acids, however, are weaker conductors due to their partial ionization. Other factors, such as concentration, temperature, solvent, and impurities, also significantly impact the conductivity of acidic solutions. Understanding these factors is crucial in various scientific and industrial applications involving acidic solutions. The ability to accurately measure and interpret the conductivity of acids provides valuable insights into their properties and behavior, impacting fields from industrial processes to environmental monitoring. The interplay of ionization, ion mobility, and external factors creates a rich tapestry of electrical behavior within acidic solutions, highlighting the complexity and importance of this fundamental chemical property.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Verbs That Start With An S
Apr 10, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Shared In A Single Covalent Bond
Apr 10, 2025
-
How Many Kings In A Pack Of Cards
Apr 10, 2025
-
Does An Earthworm Have A Backbone
Apr 10, 2025
-
What Is The Serous Membrane That Encloses Each Lung
Apr 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Are Acids Good Conductors Of Electricity . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.