A Quadrilateral With 1 Pair Of Parallel Sides
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
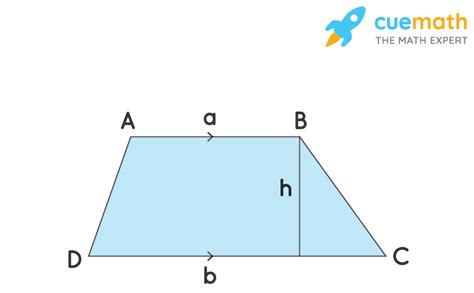
Table of Contents
A Quadrilateral with 1 Pair of Parallel Sides: Understanding Trapezoids
A quadrilateral, by definition, is a polygon with four sides and four angles. Within this broad category lie various specific shapes, each with its unique properties. One such shape is the trapezoid, a quadrilateral possessing exactly one pair of parallel sides. Understanding the properties, types, and applications of trapezoids is crucial for anyone studying geometry and its practical applications. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of trapezoids, exploring their characteristics, calculations, and real-world examples.
Defining the Trapezoid: More Than Just Parallel Sides
The defining characteristic of a trapezoid is the presence of exactly one pair of parallel sides. These parallel sides are known as bases, often labeled as b₁ and b₂. The other two sides, which are not parallel, are called legs. It's crucial to distinguish a trapezoid from a parallelogram, which has two pairs of parallel sides. A trapezoid is a more general quadrilateral, encompassing parallelograms as a special case.
Let's further clarify the definition: a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides is not a trapezoid; it's a parallelogram. This seemingly simple distinction forms the foundation of many geometrical proofs and calculations.
Key Terminology: Understanding the Parts of a Trapezoid
To effectively work with trapezoids, familiarizing yourself with the following terminology is essential:
- Bases (b₁ and b₂): The two parallel sides of the trapezoid.
- Legs: The two non-parallel sides.
- Base Angles: The angles formed by a base and a leg. Each base has two base angles.
- Altitude (h): The perpendicular distance between the two bases.
- Median (m): The line segment connecting the midpoints of the legs. The length of the median is the average of the lengths of the bases: m = (b₁ + b₂)/2.
Types of Trapezoids: Exploring Variations
While all trapezoids share the fundamental characteristic of having one pair of parallel sides, they can be further classified into different types based on the lengths of their legs and the angles they form:
1. Isosceles Trapezoid: Elegance in Symmetry
An isosceles trapezoid is a trapezoid where the two legs are congruent (equal in length). This symmetry leads to several interesting properties:
- Base angles are congruent: The two base angles adjacent to each base are equal in measure.
- Diagonals are congruent: The lengths of the diagonals are equal.
This symmetry simplifies many calculations and geometric proofs involving isosceles trapezoids.
2. Right Trapezoid: A Right Angle Perspective
A right trapezoid is a trapezoid where at least one leg is perpendicular to both bases. This creates a right angle between a leg and one of the bases. This simplifies area calculations significantly, as the altitude is directly one of the legs.
3. Scalene Trapezoid: The General Case
A scalene trapezoid is a trapezoid where all four sides have different lengths, and consequently, all four angles have different measures. This is the most general type of trapezoid, encompassing trapezoids that are neither isosceles nor right. While lacking the geometric symmetries of the other types, its general nature allows for a broad range of applications.
Calculating the Area of a Trapezoid: A Practical Approach
The area of a trapezoid is calculated using a simple formula that considers the lengths of the bases and the altitude:
Area = (1/2) * (b₁ + b₂) * h
Where:
- b₁ and b₂ are the lengths of the two bases.
- h is the height (altitude) of the trapezoid.
This formula is derived from dividing the trapezoid into two triangles and a rectangle, calculating the area of each, and summing them together. Understanding this derivation provides valuable insight into the formula’s underlying logic.
Calculating the Area of Special Trapezoids: Simplifying the Process
For specific types of trapezoids, the area calculation can be further simplified:
- Isosceles Trapezoid: While the basic formula still applies, the symmetry of an isosceles trapezoid can sometimes lead to alternative calculation methods.
- Right Trapezoid: The altitude (h) is equal to the length of one of the legs, simplifying the area formula significantly.
Calculating the Perimeter of a Trapezoid: A Straightforward Calculation
The perimeter of a trapezoid, like any polygon, is simply the sum of the lengths of all four sides:
Perimeter = b₁ + b₂ + leg₁ + leg₂
This calculation is straightforward and requires only the lengths of the four sides.
Applications of Trapezoids: From Architecture to Art
Trapezoids are surprisingly common in various aspects of our daily lives, appearing in a number of unexpected places:
- Architecture: Many buildings feature trapezoidal windows, roofs, and structural elements. The unique shape contributes to both aesthetics and structural stability. Think of the sloping sides of many traditional houses or the unique designs of modern buildings.
- Civil Engineering: Trapezoidal channels are used for irrigation and drainage systems. Their shape helps to efficiently manage water flow.
- Art and Design: Trapezoids appear in various artistic creations, from paintings and sculptures to graphic design and computer-aided design (CAD) applications. The shape's inherent visual interest contributes to its popularity.
- Everyday Objects: Trapezoidal shapes can be found in everyday objects such as furniture, toys, and even some types of food packaging.
Advanced Properties and Theorems: Diving Deeper into Geometry
While the basic properties and calculations are crucial for a foundational understanding, several more advanced concepts enhance our comprehension of trapezoids:
- Midsegment Theorem: The median of a trapezoid is parallel to both bases and its length is equal to the average of the lengths of the bases.
- Area and Similarity: Similar trapezoids have proportional areas, a property that’s useful in scaling and mapping applications.
- Inscribed Circles: Certain trapezoids, particularly isosceles trapezoids, can have inscribed circles. This property relates to the trapezoid’s shape and the lengths of its sides.
Solving Problems Involving Trapezoids: Putting Knowledge into Practice
To solidify your understanding of trapezoids, let's explore a few example problems:
Problem 1: Find the area of a trapezoid with bases of length 8 cm and 12 cm, and an altitude of 5 cm.
Solution: Using the area formula, Area = (1/2) * (8 + 12) * 5 = 50 cm².
Problem 2: An isosceles trapezoid has bases of 6 cm and 10 cm, and legs of 5 cm each. Find its perimeter.
Solution: Perimeter = 6 + 10 + 5 + 5 = 26 cm.
Problem 3: A right trapezoid has bases of 4 cm and 7 cm and a leg perpendicular to both bases of length 3 cm. Find its area.
Solution: Since it's a right trapezoid, the altitude is 3 cm. Area = (1/2) * (4 + 7) * 3 = 16.5 cm².
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of the Trapezoid
The trapezoid, though a seemingly simple quadrilateral, offers a wealth of geometrical properties and practical applications. Understanding its defining characteristics, various types, and calculation methods is crucial for anyone studying geometry or working with applications involving spatial reasoning. From the architectural marvels of buildings to the efficient design of irrigation systems, the trapezoid's influence extends far beyond the classroom. By mastering the concepts presented here, you'll gain a deeper appreciation for the elegance and utility of this fundamental geometric shape. Further exploration into more advanced properties and theorems will unlock even more insights into the world of trapezoids and their place in the broader field of geometry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Largest Cell Of The Human Body
Mar 25, 2025
-
Common Multiples Of 12 And 16
Mar 25, 2025
-
99 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 25, 2025
-
Relation Between Angular Acceleration And Linear Acceleration
Mar 25, 2025
-
John Drives To His Workplace And Back Home
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Quadrilateral With 1 Pair Of Parallel Sides . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
