5/2 Simplified As A Mixed Number
Juapaving
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
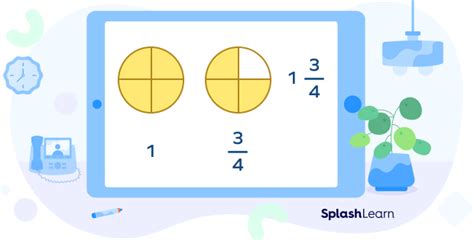
Table of Contents
5/2 Simplified as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The seemingly simple fraction 5/2 presents a great opportunity to delve into the world of fractions, specifically focusing on converting improper fractions into mixed numbers. This comprehensive guide will not only explain how to simplify 5/2 as a mixed number but also explore the underlying concepts, provide practical examples, and offer tips for mastering fraction manipulation.
Understanding Fractions: A Quick Recap
Before we dive into simplifying 5/2, let's refresh our understanding of fractions. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's composed of two key components:
- Numerator: The top number, indicating the number of parts we have.
- Denominator: The bottom number, indicating the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
Fractions can be categorized into two types:
- Proper Fractions: The numerator is smaller than the denominator (e.g., 1/2, 3/4).
- Improper Fractions: The numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., 5/2, 7/3). Improper fractions are often easier to visualize and work with when converted into mixed numbers.
Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
An improper fraction represents a value greater than or equal to one. Converting it to a mixed number provides a more intuitive representation showing the whole number part and the remaining fractional part. This is done through division.
Steps to Convert an Improper Fraction to a Mixed Number:
- Divide the numerator by the denominator: This will give you a quotient (whole number) and a remainder.
- The quotient becomes the whole number part of your mixed number.
- The remainder becomes the numerator of the fractional part.
- The denominator remains the same.
Let's illustrate this with the fraction 5/2:
- Divide: 5 ÷ 2 = 2 with a remainder of 1.
- Whole number: The quotient is 2.
- Numerator: The remainder is 1.
- Denominator: The denominator stays as 2.
Therefore, 5/2 simplified as a mixed number is 2 1/2.
Visualizing 5/2
Understanding the concept visually can solidify the idea. Imagine you have 5 pizzas, each cut into 2 equal slices. You can make 2 complete pizzas (2 whole pizzas) using 4 of the slices (2 slices/pizza x 2 pizzas = 4 slices). You'll have 1 slice left over, which is 1 out of the 2 slices per pizza. Hence, you have 2 whole pizzas and 1/2 a pizza, represented as 2 1/2.
Working with Mixed Numbers: Addition and Subtraction
Mixed numbers are frequently used in everyday calculations. Let's explore how to perform basic arithmetic with them.
Addition:
To add mixed numbers, you can either convert them to improper fractions first or add the whole numbers and fractional parts separately.
Example: Add 2 1/2 + 1 1/4
-
Method 1 (Improper Fractions):
- Convert 2 1/2 to an improper fraction: (2 x 2 + 1) / 2 = 5/2
- Convert 1 1/4 to an improper fraction: (1 x 4 + 1) / 4 = 5/4
- Add the improper fractions: 5/2 + 5/4 = 10/4 + 5/4 = 15/4
- Convert the result back to a mixed number: 15/4 = 3 3/4
-
Method 2 (Separate Parts):
- Add the whole numbers: 2 + 1 = 3
- Find a common denominator for the fractions: 1/2 + 1/4 = 2/4 + 1/4 = 3/4
- Combine the whole number and fraction: 3 + 3/4 = 3 3/4
Subtraction:
Subtraction follows a similar approach. Converting to improper fractions is often simpler for more complex subtractions.
Example: Subtract 1 1/4 from 2 1/2.
-
Method 1 (Improper Fractions):
- Convert 2 1/2 to 5/2
- Convert 1 1/4 to 5/4
- Subtract: 5/2 - 5/4 = 10/4 - 5/4 = 5/4
- Convert to a mixed number: 5/4 = 1 1/4
-
Method 2 (Separate Parts):
- Subtract whole numbers: 2 - 1 = 1
- Subtract fractions: 1/2 - 1/4 = 2/4 - 1/4 = 1/4
- Combine: 1 + 1/4 = 1 1/4
Multiplication and Division of Mixed Numbers
Multiplication and division of mixed numbers are usually simplified by first converting them to improper fractions.
Multiplication:
Multiply the numerators and then the denominators. Simplify the result if possible.
Example: Multiply 2 1/2 by 1 1/4
- Convert to improper fractions: 5/2 x 5/4 = 25/8
- Convert back to mixed number: 25/8 = 3 1/8
Division:
Invert the second fraction (reciprocal) and multiply.
Example: Divide 2 1/2 by 1 1/4
- Convert to improper fractions: 5/2 ÷ 5/4 = 5/2 x 4/5 = 20/10 = 2
Real-World Applications of Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Fractions and mixed numbers are integral parts of various real-world scenarios:
- Cooking and Baking: Recipes often require fractional measurements of ingredients.
- Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements using fractions are crucial for accuracy.
- Finance: Dealing with percentages and portions of money.
- Data Analysis: Representing proportions and parts of a whole.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
This guide provided a foundation for understanding and working with mixed numbers, specifically focusing on simplifying 5/2. To further enhance your skills, consider exploring:
- Equivalent Fractions: Understanding that multiple fractions can represent the same value.
- Simplifying Fractions: Reducing fractions to their lowest terms.
- Working with decimals: Converting fractions to decimals and vice versa.
- Order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS): Applying the correct order when solving complex expressions involving fractions.
Conclusion
Mastering the conversion of improper fractions to mixed numbers, as demonstrated with 5/2 becoming 2 1/2, is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This ability is not just about manipulating numbers; it is about understanding the underlying concepts of parts and wholes, which have widespread practical applications in various aspects of life. By understanding these concepts and practicing regularly, you'll build confidence and proficiency in handling fractions and mixed numbers with ease. Remember to visualize the concepts whenever possible, and don’t be afraid to experiment and explore!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Radius Of Circle With Centre N
Apr 04, 2025
-
Pick Up The Incorrect Statement From The Following
Apr 04, 2025
-
Fe Iron Rusts Physical Or Chemical Change
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Eye And Ear Are Part Of
Apr 04, 2025
-
Meiosis I And Meiosis Ii Different
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 5/2 Simplified As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
