30 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
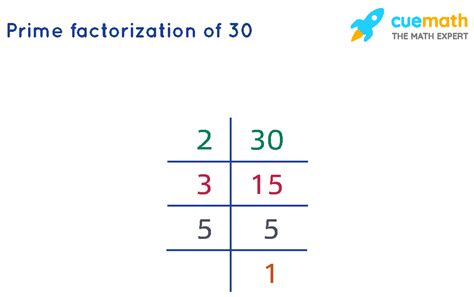
Table of Contents
30 as a Product of Prime Factors: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple number 30 holds a fascinating secret within its numerical structure. It's not just a number; it's a prime factorization puzzle, a building block of arithmetic, and a gateway to understanding more complex mathematical concepts. This article will delve into the world of prime factorization, exploring why 30 is special and how its prime factorization reveals fundamental truths about number theory. We'll also explore the practical applications of understanding prime factorization beyond the classroom.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we embark on the journey of factoring 30, let's establish a solid foundation by defining prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has only two distinct positive divisors: 1 and itself. This means it's not divisible by any other number without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all other numbers, and their properties have captivated mathematicians for centuries.
The Significance of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers are fundamental because every natural number greater than 1 can be expressed uniquely as a product of prime numbers. This is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This theorem is crucial because it establishes the uniqueness of prime factorization. It means that no matter how you factor a number, you'll always arrive at the same set of prime factors. This uniqueness is a cornerstone of many mathematical fields.
Prime Factorization of 30
Now, let's address the main topic: the prime factorization of 30. This process involves breaking down the number 30 into its prime components. We can do this using a method called a factor tree.
Method 1: Factor Tree
- Start by finding any two factors of 30. A simple choice is 2 and 15:
30 / \ 2 15 - Now, examine each factor. 2 is a prime number, so we can't break it down further. However, 15 is not prime; it's divisible by 3 and 5:
30 / \ 2 15 / \ 3 5 - Both 3 and 5 are prime numbers, so we've reached the end of our factorization.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 30 is 2 x 3 x 5.
Method 2: Division by Prime Numbers
Alternatively, we can find the prime factorization by repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number that divides it evenly.
- Start with 30. The smallest prime number is 2, and 30 is divisible by 2: 30 / 2 = 15.
- Now we have 15. The smallest prime number that divides 15 is 3: 15 / 3 = 5.
- Finally, 5 is a prime number, so the process is complete.
This method also gives us the prime factorization: 2 x 3 x 5.
The Uniqueness of 30's Prime Factorization
As the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic guarantees, the prime factorization of 30 is unique. No matter what method we use, we always end up with the same prime factors: 2, 3, and 5. This uniqueness is extremely important in various mathematical applications.
Implications of Unique Prime Factorization
The uniqueness of prime factorization has far-reaching consequences:
- Simplifying Fractions: When simplifying fractions, finding the prime factorization of the numerator and denominator allows us to easily identify common factors to cancel out.
- Finding the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): The prime factorization method is the most efficient way to determine the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers.
- Cryptography: Prime factorization plays a crucial role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography algorithms like RSA. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components is the basis for the security of these systems.
Applications of Prime Factorization Beyond Mathematics
While the theoretical implications are significant, prime factorization also finds practical applications in various fields:
- Computer Science: Prime numbers and factorization are used in hash tables, random number generators, and other algorithms crucial for efficient computer operations.
- Coding Theory: Prime numbers help in designing efficient error-correcting codes used in data transmission and storage.
- Chemistry: Prime factorization can be relevant in understanding molecular structures and chemical reactions. The number of atoms in a molecule, for example, can be analyzed in terms of its prime factorization.
30: A Number Rich in Divisors
The prime factorization of 30 reveals information about its divisors. Since 30 = 2 x 3 x 5, we can find its divisors by considering combinations of these prime factors and 1. Its divisors are: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, and 30. The number of divisors is obtained by adding 1 to each exponent in the prime factorization (all exponents are 1 in this case), and multiplying the results: (1+1)(1+1)(1+1) = 8 divisors.
Exploring Further: Beyond 30
Understanding the prime factorization of 30 provides a strong foundation for exploring the prime factorization of larger numbers. The same principles apply—repeatedly dividing by the smallest prime number until only prime numbers remain. This process can be used to factorize any positive integer, solidifying the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic's importance.
Conclusion: The Enduring Power of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple act of finding the prime factors of 30 (2 x 3 x 5) unveils a world of mathematical depth and practical applications. This exploration highlights the fundamental role of prime numbers in number theory, cryptography, computer science, and beyond. Understanding prime factorization not only enhances mathematical skills but also provides a glimpse into the elegant structure that underlies seemingly simple numbers. The power of prime factorization is a testament to the beauty and usefulness of fundamental mathematical concepts. It's a journey that begins with a single number but leads to a deeper understanding of the world of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Complement Of A 45 Degree Angle
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Secondary Structure Of Dna
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Multiples Of 40
Mar 19, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 60 And 24
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Is Frequency And Amplitude Related
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 30 As A Product Of Prime Factors . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
